Big Bear Lake
|
Big Bear Lake Great Bear Lake, Grand lac de l'Ours |
||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Déline in November 2006 | ||
| Geographical location | Northwest Territories ( Canada ) | |
| Tributaries | Haldane River , Dease River , Camsell River , Johnny Hoe River , Whitefish River , Big Spruce River , Bloody River | |
| Drain | Great bear river | |
| Places on the shore | Deline , Port Radium | |
| Data | ||
| Coordinates | 65 ° 55 ′ N , 120 ° 35 ′ W | |
|
|
||
| Altitude above sea level | 156 m | |
| surface | 31,153 km² | |
| length | 293 km | |
| width | 188 km | |
| volume | 2236 km³ | |
| Maximum depth | 446 m | |
| Middle deep | 72 m | |
| Catchment area | 145,000 km² | |
|
||
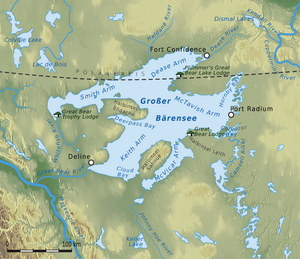
| Map of the Great Bear Lake | ||
The Great Bear Lake ( English Great Bear Lake ; French Grand lac de l'Ours ; Slavey Sahtú ) is the largest lake in the area of the Northwest Territories in Canada , the fourth largest lake in North America and thus the largest lake in North America outside the Great Lakes area . It is located in the Déline District of the Sahtu Region .
The lake extends on both sides of the Arctic Circle ; its water surface is at an altitude of 156 m . It has a surface of 31,153 km² and a total volume of 2236 km³. The average depth is 72 m; at the deepest point in the eastern part (west of Port Radium ) the lake is 446 m deep. This means that the bottom of the lake is 290 m below sea level. So this is a crypto-depression .
The lake is widely ramified and can be divided into several so-called arms. These are in the northern part of the Smith arm with the Whitefish River as a tributary and east of it the Dease arm. The main part of the lake consists of the McTavish Arm, which extends between the peninsulas Ehdacho (to the west) and Sahoyúé (to the south) and Port Radium to the east. The two southern arms are the McVicar Arm in the southeast and the Keith Arm with the Great Bear River ( Sahtúdé ) as a drain, which flows into the Mackenzie River . The sea arms were named after members of the Hudson's Bay Company who accompanied John Franklin's Arctic expeditions from 1819 to 1822, namely after Peter Warren Dease (1788–1863), Robert McVicar, John McTavish, Edward Smith and George and James Keith.
The Sahtú people who belong to the group of Dene are named after the lake. The only larger settlement on the Great Bear Lake is Déline on the west bank of the lake. Port Radium to the east was important in the 20th century as a transshipment port for the nearby uranium and silver mines Eldorado and Echo Bay . Some of the uranium extracted was used during the Second World War for the Manhattan Project , i.e. the construction of the first atomic bombs . After the mining operations ceased in 1982, the settlement was abandoned. In the north-east of the lake, the Fort Confidence fur trading post was built in 1837 , but it was abandoned around the turn of the century and fell victim to a fire by 1911.
The peninsulas Ehdacho and Sahoyúé protruding into the lake were declared National Historic Sites of Canada on September 22, 1997 .
The lake is in 2016 established Biosphere Reserve by TSA Tué .
gallery
The Grizzly Bear Mountain, a sacred mountain to Saintu Dené, who are part of the Slavey , before 1936
Web links
- Great Bear Lake ( English, French ) In: The Canadian Encyclopedia .
- International Lake Environment Committee: Great Bear Lake (English)
- Lionel Johnson: The Great Bear Lake: Its Place in History , 1975 (PDF document)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Big Bear River at the gauge at the outlet from the Big Bear Lake - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET
- ^ Sahtu Settlement Area
- ↑ Saoyú-? Ehdacho National Historic Site of Canada. In: Canadian Register of Historic Places. Retrieved May 25, 2019 .
- ↑ UNESCO Biosphere Reserves. Tsá Tué. In: Ecological Sciences for Sustainable Development. UNESCO , accessed on May 25, 2019 .