Guanethidine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
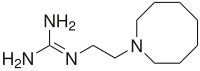
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Guanethidine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 22 N 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 198,31 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Guanethidine (trade name: Thilodigon (D), manufacturer: Alcon ) is a medicinal substance that is used in high blood pressure therapy, i.e. as an antihypertensive agent , and as a local anesthetic to block a nerve. Due to its mechanism of action, which is based on influencing the sympathetic nervous system , it is also known as an antisympathotonic .
pharmacology
Mode of action and pharmacokinetics
The mechanism of action of guanethidine is based on reducing the release of the messenger substance noradrenaline from the endings of the nerve cells into the synaptic cleft . Initially, more norepinephrine is released. Due to its high affinity for the noradrenaline transport systems in the vesicle membrane and the axon membrane of the varicosity , the reuptake of the released noradrenaline is prevented and the guanethidine is stored instead. Guanethidine, however, does not have the effect of noradrenaline, which is otherwise by means of α 1 - Adrenozeptorenaktivierung effected over vasoconstriction a blood pressure increase. Pain therapy also makes use of the fact that guanethidine inhibits the efferent sympathetic nerve conduction. This application, known as “guanethidine blockade”, is limited to the extremities. After putting on a tourniquet and then intravenous injection, the effect lasts for about 24-72 hours. Guanethidine does not penetrate the central nervous system (CNS).
Side effects
In stressful situations, the stress hormone adrenaline , which is stored and released by guanethidine, is released from the adrenal medulla , which in turn increases blood pressure. However, since every long-term disconnection of the sympathetic system results in an over-sensitivity of the successor organs to catecholamines - such as adrenaline - a sudden blood pressure crisis can occur in the event of emotional upheaval.
In addition, ejaculation disorders in the form of aspermatism can occur after administration of guanethidine ; In this case, despite an orgasm, the ejaculation does not occur, whereby this is not a disruption of the ejaculation mechanism, but a drying up of the production of sperm liquor due to a total, isolated, but reversible secretion inhibition of the so-called sex glands, especially the prostate and vesicle glands.
Interactions
Methylphenidate can reduce the hypotensive effects of guanethidine. On the other hand, the initial sympathomimetic effect of guanethidine can be enhanced.
Related links
- Guanethidine sulfate
- Guanethidine monosulfate
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for guanethidine sulfate: CAS number: 60-02-6, EC number: 200-452-0, ECHA InfoCard: 100.000.411 , PubChem : 65328 , ChemSpider : 58812 , DrugBank : DB01170 , Wikidata : Q27122278 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for guanethidine monosulfate: CAS number: 645-43-2, EC number: 211-442-0, ECHA InfoCard: 100.010.403 , PubChem : 86471 , ChemSpider : 77986 , DrugBank : DB01170 , Wikidata : Q27122277 .