Hydrazones
Hydrazones are derivatives of aldehydes or ketones . In analogy to the imines, they arise in a condensation reaction by reaction of the carbonyl compounds with hydrazine or with its derivatives (e.g. phenylhydrazine , 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, etc.). The scheme shows the reaction of one equivalent of the carbonyl compound with hydrazine, which leads to the hydrazone. If two equivalents of the carbonyl compound are reacted with hydrazine, the hydrazone is also formed first, which can then react further to form an azine in a second step .
R 1 and R 2 can be different or the same organic radicals, including hydrogen atoms.
meaning
The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazones were of particular analytical importance; as carbonyl derivatives which crystallize well, they enable the identification of carbonyl compounds (especially of aldehydes and ketones ) via the melting point of the respective 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone.
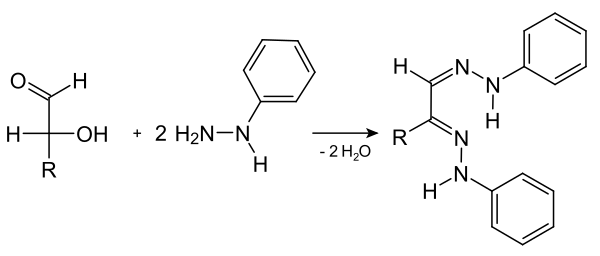
History of the formation of the Osazonen
The phenylhydrazones of sugars , also known as osazones , are of historical importance . Emil Fischer discovered phenylhydrazine in 1874 while working on the diazotization of aniline . It was later used to characterize sugars. Aldoses as well as ketoses whose keto group is at C-2 form double hydrazones at the - and - atom with three equivalents of phenylhydrazine . The formation of the Osazone is associated with a redox reaction ; one mole of phenylhydrazine is reduced to aniline and ammonia , one hydroxyl group of the monosaccharide is oxidized to a carbonyl group .
properties
With a suitable substitution pattern, hydrazones are subject to the azo hydrazone tautomerism .
Syntheses
The hydrazones are of preparative importance in the Wolff-Kishner reaction . When deprotonated, they split off nitrogen (N 2 ) and thus allow the selective reduction of ketones and aldehydes to alkanes .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 2: Cm-G. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-440-04512-9 , p. 973.
- ↑ Hans Beyer and Wolfgang Walter : Organische Chemie , S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart, 1984, p. 203, ISBN 3-7776-0406-2 .
- ↑ Ivan Ernest: Binding, Structure and Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry , Springer-Verlag, 1972, p. 129, ISBN 3-211-81060-9 .