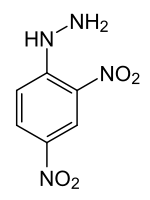
2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 6 N 4 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
dark orange to dark red odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 198.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.84 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
200 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine is a chemical compound from the group of aromatic hydrazines with the empirical formula C 6 H 6 N 4 O 4 .
Extraction and presentation
It can be prepared by reacting 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene with hydrazine .
properties
The compound itself is a red-orange, odorless solid. Dry 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine is explosive; the decomposition produces nitrous gases. It is phlegmatized with water, i. That is, about 0.5 ml of water per gram of DNPH are added to the commercially available product in order to make the substance storable and transportable. The connection is usually moistened (e.g. with a water content of 33%) so that it is no longer explosive (therefore no GHS hazardous substance labeling as explosive).
use
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine is used as a detection reagent for the carbonyl group , a functional group in organic chemical compounds. The reaction is specific for carbonyl groups of aldehydes and ketones , but no reaction takes place with carboxylic acids , amides or esters . The first step is a nucleophilic addition of the NH 2 group to the carbonyl group, after which a molecule of water is split off. In this condensation reaction , aldehydes and ketones react to form the corresponding 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone (C = N – NHAr). Mechanistically, this condensation reaction with elimination of water corresponds to the formation of imines from primary amines and aldehydes or ketones.
If the reaction of the compound to be tested with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine results in the formation of a precipitate under slightly acidic conditions, the sample was positive. The hydrazones shown have different but sharp melting points, which makes it possible to identify the hydrazone (and thus the starting product) by measuring the melting point and comparing it with tabulated values.
Because of its property as a detection reagent for the carbonyl group, 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine is used with the DNPH method to measure emissions of aldehydes and ketones in exhaust gases.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, moistened with at least 30% by mass of water in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 17, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 12, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on (2,4-Dinitrophenyl) hydrazine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd Edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, p. 523, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 .
- ↑ https://www.appLICH.com/en/shop/product-detail/as/24-dinitrophenylhydrazin-mit-33-h2o-angefuchteret-reag-ph-eur-pa/
- ↑ VDI 3862 sheet 2: 2000-12 measurement of gaseous emissions; Measuring aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes and ketones by the DNPH method; Gas washing bottle method (Gaseous emission measurement; Measurement of aliphatic and aromatic aldeydes and ketones by DNPH method; Impinger method). Beuth Verlag, Berlin, p. 5.


