IC 4593
|
Planetary Nebula IC 4593 |
|
|---|---|
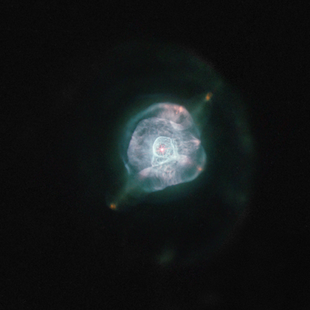
|
|
| Image taken with the Hubble Space Telescope | |
| AladinLite | |
| Constellation | Hercules |
|
Position equinox : J2000.0 |
|
| Right ascension | 16h 11m 44.5s |
| declination | + 12 ° 04 ′ 17 ″ |
| Appearance | |
| Apparent brightness (visual) | 10.7 likes |
| Apparent brightness (B-band) | 10.9 mag |
| Angular expansion | 0.7 ′ × 0.7 ′ |
| Central star | |
| Physical data | |
| distance | 12,000 ly |
| history | |
| discovery | Williamina Fleming |
| Date of discovery | 1907 |
| Catalog names | |
| IC 4593 • PK 025 + 40 1 • PN G025.3 + 40.8 • IRAS 16093 + 1211 | |
IC 4593 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Hercules . The bright center of IC 4593 has an angular extent of about 17 ", whereby this planetary nebula is still surrounded by a much weaker, but with 120", clearly larger halo. A white dwarf , which is quite hot at 40,000 K and has a rather average size at 0.7 solar masses, shines in IC 4593 . This ionizes the surrounding gas clouds through its strong UV radiation and excites them to glow, whereby the typical turquoise light of the double ionized oxygen [O III] dominates this light. IC 4593 is about 3.7 kpc (about 12,000 light years ) from us. The designation is a number in the index catalog (IC).
Visual observation
IC 4593 is a somewhat inconspicuous planetary nebula and not easy to find in the "no man's land" between Hercules, snake bearer and snake. It is best to move your telescope roughly in the right direction and orientate yourself on the very conspicuous, 7.65 mag bright double star GSC 0953-0844. IC 4593 is located 11 '10 "of this in a north-westerly direction. At 100-fold magnification in medium-sized telescopes around 10" aperture, IC 4593 looks more like a "foggy star". Only at a magnification of 260x and looking indirectly can you see the very weakly shining, structureless gas nebula around a turquoise central star with some difficulty.