Isoprothiolane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
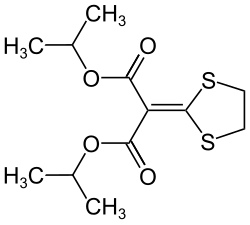
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Isoprothiolane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 18 O 4 S 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
|
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 290.40 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (0.054 g l −1 at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Isoprothiolane is a chemical compound from the group of dithiolanes and 1974 by Nihon Noyaku introduced fungicide . Isoprothiolane has a noticeable ketene di thioacetal structure.
Extraction and presentation
Isoprothiolane can be prepared from diisopropylmalonate , which reacts with carbon disulfide in the presence of sodium hydride . The product reacts further with 1,2-dibromoethane to form isoprothiolane.
use
Isoprothiolane is a systemic fungicide with curative and protective effects. The active ingredient is used in rice cultivation to combat various fungal diseases such as rice blight .
It is also used to treat fatty liver syndrome in cattle.
Admission
No plant protection products containing this active ingredient are permitted in the EU or Switzerland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on isoprothiolane. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on January 8, 2015.
- ↑ a b Isoprothiolane data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Hiroki Ota: Historical Development of Pesticides in Japan, pp. 80-81.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 734 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Takashi Hirooka, Yukio Miyagi, Fujio Araki, Hitoshi Kunoh, Hiroshi Ishizaki: The effect of isoprothiolane on the emergence of infection pegs from appressoria of Pyricularia oryzae . In: Pesticide Science . tape 13 , no. 4 , August 1982, p. 379-386 , doi : 10.1002 / ps.2780130407 .
- ↑ Y. Shimada, H. Katamoto, S. Ishida, K. Kobayashi, H. Tohzyoh: Therapeutic effect of isoprothiolane on bovine fat necrosis. In: Nihon juigaku zasshi. The Japanese journal of veterinary science. Volume 50, Number 5, October 1988, ISSN 0021-5295 , pp. 1017-1024, PMID 3199611 .
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Isoprothiolane in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 26, 2016.
