Potassium hydrogen sulfate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
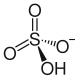
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium hydrogen sulfate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Potassium bisulfate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | KHSO 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 136.17 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.24 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
195 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (490 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Potassium hydrogen sulfate KHSO 4 is an acidic potassium salt of sulfuric acid . It occurs when sulfuric acid is only 50% neutralized with potassium hydroxide and the solution is evaporated. The product is corrosive, crystalline and contains potassium ions as well as the hydrogen sulfate anion HSO 4 - .
synthesis
The synthesis of potassium and sodium hydrogen sulfate is achieved by the action of moderately warm, concentrated sulfuric acid on potassium or sodium chloride . The gas hydrogen chloride is produced as a by-product of this displacement reaction :
properties
The white, crystalline solid dissolves easily in water to form an acidic solution:
If the sulfuric acid potassium sulfate is heated , it is converted into potassium disulfate with the release of water ( dehydration ) :
With further heating, the potassium disulfate breaks down into potassium sulfate and sulfur trioxide :
use
Potassium hydrogen sulfate, like the cheaper sodium hydrogen sulfate, is used as an acidic drain cleaner . Lime is dissolved in a displacement reaction .
Furthermore, potassium hydrogen sulfate serves as a detection reagent for acetates. Acetate ions (CH 3 COO - ) can be detected by grinding the salt, which is assumed to be an acetate, with potassium hydrogen sulfate in a mortar . The proton (H + ) of the hydrogen sulfate ion is transferred to the acetate ion. Acetic acid is formed, which can easily be identified by its typical odor.
- Acetate is protonated by hydrogen sulfate. Acetic acid and sulfate are formed .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f record with potassium hydrogen sulfate in the GESTIS database of IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Potassium Hydrogensulphate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .






