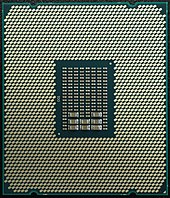
Land Grid Array
A land grid array ( LGA ) is a connection system for integrated circuits (IC, integrated circuit ).
In the LGA system, the connections of the integrated circuit are implemented on its underside in the form of a checkerboard-like field ( English grid array ) of contact surfaces ( English country ). It is closely related to the Pin Grid Array (PGA), which takes the contact surfaces known "legs" ( English pin has), and Ball Grid Array , which (BGA) solder uses beads. Another related design is the Ceramic Column Grid Array .
LGA processors are mostly placed on sockets that contain resilient contacts, which results in less mechanical stress on the contacts. In some cases, however, they are also soldered directly like PGA ICs . BGA-ICs, on the other hand, are only intended for soldering, they bring the necessary solder with them in the form of solder balls. All three variants are used for ICs with over a hundred to over four thousand contacts.
history
For x86 processors, the Land Grid Array was introduced by Intel in June 2004 as Socket 775 (also LGA775 ) for the Pentium 4 series with Prescott core, and from 2006 it was also used by competitor AMD for Socket F intended for servers and workstations introduced. Other CPU sockets that are built in LGA design are socket 771 , which is also intended for servers, and socket 1150 , socket 1151 , socket 1155 , socket 1156 , socket 1366 , socket 2011 and socket 2066 from Intel. LGA technology has been used by Sun Microsystems since the mid-1990s. B. used in the UltraSPARC processors.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Land Grid Array (LGA) - Socket and Package Technology - Handling, Inspection, & Integration Module. Intel, September 2009, accessed December 4, 2016 .