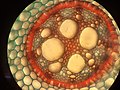
Vascular bundle
Vascular bundles (fascicles) are conduction pathways for the long-distance transport of water, dissolved substances and organic substances ( assimilates , mainly sugar) in the shoot , in the leaf and in the roots of higher plants ( vascular plants ). Vascular bundles consist of the xylem (wooden part) with cell elements for water transport ( e.g. trachea and tracheids ) and the phloem (bast part, sieve part) for the transport of the assimilates with sieve cells or sieve tubes and escort cells .
Vascular bundle types
There are several types of vascular bundles
- Simple vascular bundles only consist of a sieve part or a wooden part.
- Composite vascular bundles have a sieve part and a wooden part.
- In the case of concentric vascular bundles, the sieve part lies around the wooden part (periphloematic vascular bundle), or the wooden part lies around the sieve part (perixylematic vascular bundle).
- The most common type is the so-called collateral vascular bundle, in which the sieve part is opposite the wood part (the xylempol is facing the center of the stem axis ).
- With open collateral vascular bundles, there is also a cambium between the xylem and the phloem. This arrangement occurs in dicotyledonous plants.
- If the collateral vascular bundles are closed, the cambium is absent and the vascular bundles are surrounded by a closed, sclerchymatic vascular bundle sheath. This arrangement occurs in monocotyledonous or (other) herbaceous plants.
- A special form of the collateral type is the bicollateral vascular bundle, as it occurs, for example, in the cucurbits and nightshades . Here another phloem part is added to the vascular bundle on the side facing the center of the stem axis.
- In roots the vascular bundles are combined into a radial vascular bundle system, where the wooden part is arranged like the spokes of a wheel - the bast part lies between the spokes ( actinostele ).
Closed collateral vascular bundle at Zea mays
Longitudinal section through a vascular bundle of Zea mays
Open, bicollateral vascular bundle in Cucurbita pepo
Radial vascular bundle in
Iris germanicae
literature
- Peter Sitte , Elmar Weiler , Joachim W. Kadereit , Andreas Bresinsky , Christian Körner : Textbook of botany for universities . Founded by Eduard Strasburger . 35th edition. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2002, ISBN 3-8274-1010-X .
Web links
Commons : Leitbündel - collection of images, videos and audio files