Lithium phosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
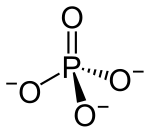
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lithium phosphate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Li 3 PO 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 115.79 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
837 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
heavy in water (0.39 g l −1 at 18 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Lithium phosphate is a chemical compound from the group of phosphates .
Occurrence
Lithium phosphate occurs naturally as a rare mineral, lithiophosphatite .
Extraction and presentation
Lithium phosphate can be obtained from alkaline (e.g. sodium hydroxide ) solutions to which a little disodium hydrogen phosphate Na 2 HPO 4 has been added. When heated, lithium phosphate precipitates out as a white precipitate in the presence of Li + (other dissolved lithium salts, e.g. lithium chloride ):
It is also possible to obtain it by reacting an aqueous suspension of lithium carbonate with phosphoric acid and then heating it to boiling. There is also a high temperature form of trilithium phosphate which is stable at normal temperatures and which, at temperatures above the transition temperature of 502 ° C, e.g. B. can be crystallized from molten lithium chloride.
properties
Lithium phosphate is a colorless solid. It crystallizes orthorhombically with the lattice constants a = 6.12 Å , b = 10.53 Å and c = 4.93 Å with the space group Pmnb (space group no. 62, position 2) . It also occurs as the lithium phosphate hemihydrate Li 3 PO 4 · ½H 2 O. The high temperature variant has a crystal structure with the space group Pcmn (no. 62, position 4) . There are also lithium metaphosphate LiPO 3 ( monoclinic , space group Pn (No. 7, position 2) ), lithium polyphosphate (P 2 O 5 : Li 2 O> 1), lithium dihydrogen phosphate LiH 2 PO 4 (orthorhombic, space group Pna 2 1 (no 33) ) and lithium dihydrogen diphosphate Li 2 H 2 P 2 O 7 .
use
Lithium phosphate can be used to detect lithium by precipitation reaction in an alkaline medium. It is still used as a component of certain enamels and as a polymer intermediate. It is also used to extract lithium iron phosphate for lithium iron phosphate batteries and doped with nitrogen as a lithium ion conductor.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b data sheet lithium phosphate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 26, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on lithium phosphate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c J. Zemann: The crystal structure of lithium phosphate, Li3PO4 . In: Acta Cryst. (1960). 13, 863-867 doi: 10.1107 / S0365110X60002132
- ↑ a b c d e entry on lithium phosphates. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 25, 2014.
- ↑ a b fmclithium: Lithium Orthophosphine Tertiary (PDF; 208 kB)
- ↑ Lithium phosphate data sheet at AlfaAesar, accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Mindat: Lithiophosphate
- ↑ HL Buff: Short textbook of inorganic chemistry according to the newer views . 1868, p. 186 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ American Mineralogist Crystal Structure Database: lithiophosphate
- ^ Karl-Heinz Lautenschläger, Werner Schröter and Andrea Wanninger: Taschenbuch der Chemie . 2005, ISBN 3-8171-1760-4 , pp. 662 ( limited preview in Google Book search).

