Mansôa
| Mansôa | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Coordinates | 12 ° 4 ′ N , 15 ° 19 ′ W | |
| Basic data | ||
| Country | Guinea-Bissau | |
| Norte | ||
| region | Oio | |
| ISO 3166-2 | GW-OI | |
| surface | 1,096.7 km² | |
| Residents | 46,046 (2009) | |
| density | 42 Ew. / km² | |
|
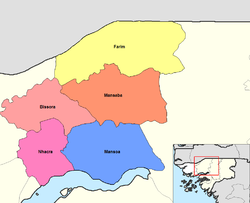
Location of the Mansôa sector (blue) in the Oio region
|
||
Mansôa is a city in the Oio region of Guinea-Bissau with 7,996 inhabitants (as of 2009). It is the seat of the sector of the same name with an area of 1097 km² and 56,585 inhabitants (as of 2009).
geography
The place is on the north side of the river of the same name, Rio Mansôa . The distance across the river to its mouth in the Atlantic at the Ilha de Pecixe is a good 100 kilometers.
Mansôa is located 60 km east of the capital Bissau.
Residents
According to the 2009 census , the city had exactly 7,996 inhabitants, the entire sector had 46,046 inhabitants.
The most important ethnic group here are predominantly the Balanta .
structure
The Mansôa sector comprises a good 150 localities, mostly rural villages ( Tabancas ).
The sector capital Mansôa is divided into eight, with subdivisions 14 districts ( Bairros ). The most important locations in the sector also include:
- Ansonhe
- Bindur (three villages)
- Binibaque (three villages)
- Bissa
- Cubui (two villages)
- Cussana (three villages)
- Cutia de Cima
- Enxale de Cima Flaque Iala
- Ga - Mamudo de Cima
- Jugudul
- Porto Gole (this is where the first European entered today's Guinea-Bissau in 1456)
- Sansanto
- Uncome Ndate
Town twinning
-
 Portugal : Matosinhos (since 1992)
Portugal : Matosinhos (since 1992)
Economy and Infrastructure
The sector is dominated by agriculture, the most important product is rice. Local trade is also of some importance.
One of the most important radio stations in the country is the local Rádio Sol Mansi , which is widely accessible in the country.
The country road that connects Mansôa with the capital Bissau, 60 km to the west, runs over the bridge built in 1964 and renamed Ponte Amílcar Cabral after 1974 .
The city has an airfield with the ICAO code GGMS.
Culture and sights
Some colonial buildings mostly from the 1940s can be seen here, but they are often in poor condition. These include the CTT post office building, the governor's palace, the cinema, the former power station and the Casa Gouveia , a former shop. Colorful market stalls now line the main street through the city.
In nearby Porto Gole there is a monument to Diogo Gomes , who landed here in 1456 as the first Portuguese and first European in Guinea-Bissau.
Sports
The most important sports club in the sector is the Clube de Futebol "Os Balantas" football club . Since the country gained independence in 1974, the club has won the national championship of Guinea-Bissau four times . Before independence, CF Balantas even dominated the top division and won each of the national championships held between 1960 and 1972.
CF Balantas welcomes its guests to the Estádio Corca Sow in Mansôa, which can hold around 3,000 spectators .
sons and daughters of the town
- José Câmnate na Bissign (* 1953), Bishop of Bissau
Web links
swell
- ↑ a b c Inhabitants by region, sector and town by gender, 2009 census (p. 41f), PDF retrieval from the INE National Statistics Office of December 30, 2017
- ↑ Annual Statistical Report Guinea-Bissau 2015 (p. 10), PDF access from the National Statistics Office INE of December 30, 2017
- ↑ a b c Joana benzinho, Marta Rosa: À Descoberta da Guiné-Bissau . , Afectos com Letras / EU, Pombal 2015, ISBN 978-989-20-6252-5 , p. 102ff
- ↑ Inhabitants by region, sector and town by gender, 2009 census (p. 41ff), PDF access from the INE National Statistics Office of January 20, 2018
- ↑ Overview of the town twinning of Matosinhos at the Association of Portuguese Local Governments (ANMP), accessed on December 30, 2017