Mioko
| Mioko | ||
|---|---|---|
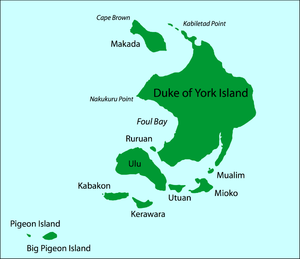
| Map of the Duke of York Islands | ||
| Waters | St. George's Canal (Papua New Guinea) | |
| Archipelago | Duke of York Islands | |
| Geographical location | 4 ° 13 '47 " S , 152 ° 27' 28" E | |
|
|
||
| length | 1.6 km | |
| width | 1.2 km | |
The small island of Mioko is located in the south of the Duke of York Islands in the St. George's Channel in the Bismarck Archipelago (Papua New Guinea). Mioko is about 1.6 kilometers long and 1.2 kilometers wide and was a starting point for the German colonization of the South Seas .
geography
The island is located at 04 ° 14 ' S , 152 ° 27' E in the Southwest Pacific and is part of Oceania . Two tectonic plates collide in this area, increasing the risk of earthquakes and tsunamis. Since the island consists of upscale coral limestone, Mioko is relatively flat and endangered by the rise in sea levels.
climate
There is a moderately humid, tropical maritime climate . Dry weather on the Duke of York Islands heralds the imminent southeast trade wind . The lowest averages of 23 ° C are in the months of June to September, the maximum temperatures of 32 ° C in the months of December and January. The humidity fluctuates between 71 and 78 percent. An average of six rainy days are recorded in December and eleven in March and April.
nature
Usually smaller forests grow on the Duke of York Islands, including the screw tree species Pandanus dubius ( called Uom by the inhabitants of the islands ). The moss Plagiochila miokensis is only found on the island of Mioko.
history
In 1776 the explorer Philipp Carteret discovered the Duke of York Islands, which he named after the brother of the English King and Duke of York, Eduard August .
The port on Mioko was already claimed for Germany in December 1878 by Captain Bartholomäus von Werner . The good natural harbor was of particular interest to the colonial efforts of the Hamburg trading houses Hernsheim and Godeffroy , and later also to the banker Adolph von Hansemann . The German flag on Mioko was hoisted on November 4, 1884 by the captain of the covered corvette SMS Elisabeth , sea captain Rudolf Schering . The archipelago was renamed Neu-Lauenburg. During the German colonial rule, there were coconut plantations on Mioko and a station of the German Trading and Plantation Society of the South Sea Islands in Hamburg ( DHPG ), later the Jaluit Society .
Otto Finsch traveled to New Guinea with the Samoa in early 1884 under the command of Eduard Dallmann and visited almost the entire north coast of New Guinea on five trips from Mioko . During his travels he discovered seven harbors and the Kaiserin Augusta River, concluded contracts for land acquisitions and hoisted the German flag. Between 1885 and 1919 Mioko was part of the German colony of German New Guinea .
From 1920 Mioko was a mandate area of the League of Nations under the administration of Australia. Mioko has belonged to the state of Papua New Guinea since independence in 1975 .
Individual evidence
- ^ The Pacific Islands Handbook . P. 239 and Pacific Islands Yearbook . 1981, p. 298
- ↑ German Colonial Lexicon 1920
- ^ The Heat Is Online: 1,000 flee as sea begins to swallow up Pacific islands
- ^ The Scottish Geographical Magazine . 1999, p. 95
- ↑ Archived copy ( memento of the original from October 16, 2006 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Climate table
- ↑ The useful plants of the island of Guam: with an introductory account of the physical features and natural history of the island, of the character and history of its people, and of their agriculture . 1905, p. 343
- ↑ Recognized species of Plagiochila in Australasia and some island groups of the Pacific Ocean ( Memento of the original from September 5, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Bartholomäus von Werner: A German warship in the South Seas. Brockhaus, Leipzig 1889.
- ↑ Samoa trips. Travels in Kaiser-Wilhelms-Land and English New Guinea in 1884 and 1885 on board the German steamer Samoa. Dallmann, Eduard, Verlag Hirt, Leipzig 1888
- ^ Ohff, Hans-Jürgen, Disastrous Ventures: German and British Enterprises in East New Guinea, Plenumn Publishing Australia, Melbourne, 2015, English
- ↑ Linke, R 2006, The influence of German surveying on the development of New Guinea, Association of Surveyors of PNG . Retrieved October 22, 2015, in English.
- ↑ The First World War and the end of German influence in the South Seas , in: Hermann Joseph Hiery (Ed.): Die Deutsche Südsee 1884-1914, Ein Handbuch . Verlag Ferdinand Schöningh, Paderborn 2001, ISBN 3-506-73912-3
- ↑ Foreign Office: Papua New Guinea: Domestic Policy