Molybdenum (III) chloride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
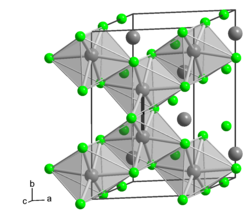
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
__ Mo 3+ __ Cl - crystal structure of α-MoCl 3 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Molybdenum (III) chloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Molybdenum trichloride |
||||||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | MoCl 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
red solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 202.30 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
3.58 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
410 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Molybdenum (III) chloride is an inorganic chemical compound of molybdenum from the group of chlorides .
Extraction and presentation
Molybdenum (III) chloride can be obtained by reacting molybdenum (V) chloride with hydrogen , tin (II) chloride or metallic molybdenum.
properties
Molybdenum (III) chloride is a copper-red to brown powder that can be kept indefinitely at room temperature under protective gas. Slow hydrolysis and oxidation occurs in moist air . It is insoluble in water, dilute hydrochloric acid, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, benzene and ethanol, but soluble in dilute nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid . Above 410 ° C, disproportionation occurs in molybdenum (II) chloride and molybdenum (IV) chloride . The connection comes in two modifications. The α-form has a monoclinic crystal structure similar to that of the aluminum (III) chloride type with the space group C 2 / m (space group no. 12) , a = 609.2 pm, b = 974.5 pm, c = 727.5 pm, β = 124.6 °. This shape consists of MoCl 6 octahedra, each octahedron being linked to three neighboring octahedra via edges. The distance to one of the neighboring Mo atoms is 274.7 pm, which implies a covalent Mo – Mo bond. The β-form also has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group C 2 / c (No. 15) , a = 611.5 pm, b = 981.4 pm, c = 1190.6 pm, β = 91.0 °. There is also a trihydrate.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Molybdenum (III) chloride, 99.95% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 2, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer: Handbook of preparative inorganic chemistry . 3., reworked. Edition. tape III . Enke, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-432-87823-0 , pp. 1531 .
- ^ A b Alan K. Mallock: Molybdenum (III) chloride . In: Robert W. Parry (Ed.): Inorganic Syntheses . tape 12 . McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1970, ISBN 07-048517-8 ( defective ) , p. 178-181 (English).
- ^ Hermann Jehn, Wolfgang Kurtz, Dietrich Schneider, Ursula Trobisch, Joachim Wagner: Mo Molybdenum . Springer Science & Business Media, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-06327-9 , pp. 281 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



