Poison berry
| Poison berry | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Poison berry ( Nicandra physalodes ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Nicandra | ||||||||||||
| Adans. | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the species | ||||||||||||
| Nicandra Physalodes | ||||||||||||
| ( L. ) Gaertn. |
The poison berry ( Nicandra physalodes , also Nicandra physalo i des ) is a species of plant from the nightshade family (Solanaceae) native to South America . It is the only species in the monotypical genus Nicandra .
description
The poison berry is an upright plant, 0.5 to 1.5 m, rarely 2 m high.
leaves
The leaves are membrane-like, narrow to broadly ovate , have an irregularly curved or wavy lobed edge and are (4) 10 to 21 (31) centimeters long and (2) 5 to 10 (20) cm wide. The leaf base is wedge-shaped to tapering to a point, the leaf stalks narrowly winged and 1.5 to 9 inches long.
The tops of the leaves have black spots 0.1 to 0.3 millimeters in diameter, evenly distributed, from which transparent cones protruding up to a millimeter in length:
- Leaf top of poison berry
blossoms
The bees-fertilized, radially symmetrical, five-fold flowers stand individually, initially upright, later nodding. The sepals , fused together in half their length, are 9 to 22 mm long. The petals are colored at the edge and the upper corolla tube between pale pink-violet to pale blue and have equally colored spots at the base of each petal. The crown is about 20 to 30 mm long and about 27 mm in diameter. The anthers are 4 to 4.5 mm long and have a few, simple and short trichomes . The five stamens are covered with long, simple trichomes at the base, short trichomes can be found on the rest of the surface. The pollen size is between 35 and 38 µm in the medium size range. The 3 to 5 mm long stylus is covered with several multicellular trichomes. The scar is about 1.5 mm long. The flowering period extends from July to October.
- Poison berry flowers
fruit
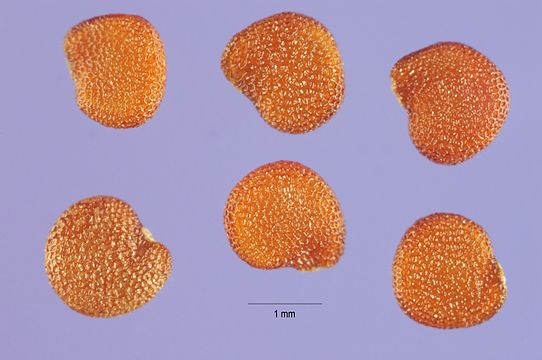
The upright fruits are formed on the elongated flower stalks. The growing calyx closes like a lampion around the developing fruit, becomes parchment-like and has a clearly visible, reticulate vein. The berries have a diameter of 10 to 15 mm and contain brownish-yellow, 1.5 to 2 mm long, flat kidney-shaped seeds with fine indentations. The embryo is rolled up, the cotyledons are shorter than the rest of the embryo.
- Fruits and seeds of the poison berry
Chromosome number
The chromosome number is where diploid and tetraploid chromosome sets have been found. There were also individual chromosome counts with and .
origin
The origin of the poison berries are the Andes of South America , where they can be found from Peru to northern Argentina . Because the plant was used as an ornamental plant, it is now often found in the wild in other areas, including the Galapagos Islands , Hawaii , the USA , India , Mozambique , Australia and Germany .
Toxicity
The poison berry is poisonous in all parts, but especially in the roots. Various alkaloids accumulate there , the main alkaloids are hygrin and tropinone . The plant also contains various withanolides , of which nicandrenone is known to have a cytotoxic effect.
- Structural formulas
use
The poison berry is rarely used as an ornamental plant in summer borders and summer flower beds. It has been in culture since the 18th century. There are some varieties, some of which have pure white flowers. Often the Blue Physalis is also grown for its properties, whiteflies or whitefly called to keep at a distance. Between z. B. Planted cabbage, the plant with its toxicity and corresponding scent does not drive away the harmful insects 100%, but reduces the infestation considerably.
literature
- Armando T. Hunziker: The Genera of Solanaceae. ARG Gantner Verlag, Ruggell, Liechtenstein 2001, ISBN 3-904144-77-4 .
- Lutz Roth, Max Daunderer, Karl Kormann: Poisonous plants plant poisons. 6th revised edition. Nikol-Verlag, Hamburg 2012, ISBN 978-3-86820-009-6 .
Web links
- Nicandra physalodes (L.) J. Gaertn., Poison berry. In: FloraWeb.de.
- Poison berry . In: BiolFlor, the database of biological-ecological characteristics of the flora of Germany.
- Nicandra physalodes (L.) Gaertn. In: Info Flora , the national data and information center for Swiss flora . Retrieved February 28, 2016.
- Thomas Meyer: Data sheet with identification key and photos at Flora-de: Flora von Deutschland (old name of the website: Flowers in Swabia )
- Short description at solanaceae.net
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Eckehart J. Jäger, Friedrich Ebel, Peter Hanelt, Gerd K. Müller (eds.): Exkursionsflora von Deutschland. Volume 5: Herbaceous ornamental and useful plants. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg 2008, ISBN 978-3-8274-0918-8 , p. 449.
- ↑ My gardening guide - Blue physalis against whitefly. Cultivation and use