Nucleosome
| Parent |
| chromosome |
| Subordinate |
|
DNA histones |
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| QuickGO |
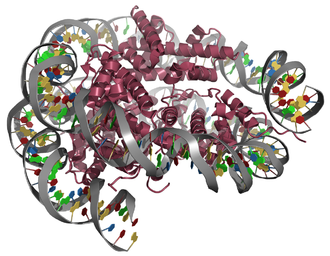
Nucleosomes form a complex of DNA and histones . This is the first stage of DNA packaging in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells ; Precursors can also be found in archaea . The sequence of nucleosome packets that hold the DNA together in chromatin as a 30 nm thick fiber is called the solenoid structure .
Structure and structure
The nucleosome is the unit of DNA and a histone octamer. The octamer consists of two copies each of the proteins H2A , H2B , H3 and H4 . 146 or 147 base pairs of DNA are wound around such a protein complex as a left-handed superhelix. The twisting of the DNA around the histone complex shortens the length of the DNA by one seventh from 68 nm to around 10 nm.
By digesting the chromatin with MNase ( endonuclease that digests free DNA), histone octamers are obtained, around which a piece of DNA approx. 147 base pairs long is wound, as well as other DNA-binding proteins and their bound DNA fragments. This unit is known as the nucleosome core particle (NCP) or nucleosome base particle.
In chromatin , the individual nucleosome core particles are connected to one another by DNA linkers of different lengths. Together with the linker histone H1, the nucleosome core particle including the linker DNA is referred to as a chromatosome . The linker histone H1 brings about a condensation of the individual nucleosomes and results in a more compact organization of the chromatin, which could be identified at least in vivo as a 30 nm fiber.
The structure of nucleosomes was pioneered by Aaron Klug's group in the 1980s. By means of X-ray structure analysis it could be shown that a tetramer of (H3) 2 (H4) 2 and two dimers of the histones H2A-H2B are present in the core particle .
discovery
Discovered by Ada and Donald Olins in electron microscopic representations of swollen cell nuclei and first presented as "ν-body" ('new particle') at the "Third Annual Meeting of the American Society for Cell Biology" in 1973, the helical shape ( solenoid structure ) became almost immediately accepted as the elementary packaging unit of the DNA in the chromatin .
In 1974 several teams, including that of Roger Kornberg , succeeded in analyzing the structure of these particles from a complex made up of eight histones , a connecting linker histone and around 160–200 base pairs of DNA. In 1975 this unit was introduced as a nucleosome . 1974 is now considered the year of birth of molecular epigenetics .
In addition to interactions that lead to the compression of the DNA, the histones also interact with one another. The nucleosome core (the "core particle") is formed from two copies of the histones H2a , H2b , H3 and H4 . 146 base pairs of DNA are wound around this protein complex in 1.65 turns. The area between two nucleosomes (the variable "left" area, which can be between 160 base pairs in yeast and 200 base pairs in higher organisms; in humans it is 50-60 base pairs) is occupied by another histone, H1 , which appears on Structure of the next higher structure (the so-called 30 nm fiber, explained e.g. in the solenoid model). The components of the nucleosome core have been highly conserved in evolution (only two amino acid residues differentiate the histone H3 in humans from that of the pea), which underscores the fundamental importance of this unit (and its modifications - see below).
Work on the structure of nucleosomes was started by Aaron Klug (Nobel Prize 1982 for crystal structure analysis of protein / nucleic acid complexes) in London at the Medical Research Council. This work led to the first structural proposal in 1984 with a relatively low resolution. Since then, the work has been systematically driven forward by Timothy Richmond , who was already involved in the first structural proposal in Klug's group in 1984, at the Institute for Molecular Biology & Biophysics at ETH Zurich . In 1997 the Richmond research group published a structure of the nucleosome with a resolution of 2.8 Å and in 2002 the structure was published with a resolution of 1.9 Å.
In 2005, the Richmond group published an X-ray crystal structure of the tetranucleosome.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Kristin Brogaard, Liqun Xi, Ji-Ping Wang & Jonathan Widom: A map of nucleosome positions in yeast at base-pair resolution. Nature, 2012, accessed June 24, 2018 .
- ↑ Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer Stryer Biochemistry In: Springer Spectrum. 7th edition, pp. 951-952
- ↑ AL Olins, MB Senior, DE Olins: Ultrastructural features of chromatin nu bodies . In: The Journal of Cell Biology . tape 68 , no. 3 , March 1976, ISSN 0021-9525 , p. 787-793 , PMID 1035912 , PMC 2109642 (free full text) - ( rupress.org [accessed November 17, 2017]).
- ↑ a b Karolin Luger , Armin W. Mäder, Robin K. Richmond, David F. Sargent, Timothy J. Richmond: Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. In: Nature. 389, No. 6648, 1997, pp. 251-260, doi: 10.1038 / 38444 .
- ↑ nobel.se: Aaron Klug - Autobiography
- ↑ TJ Richmond, JT Finch, B. Rushton, D. Rhodes, A. Klug: Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 Å resolution. In: Nature . 311, 1984, pp. 532-537, PMID 6482966 .
- ^ MM Struck, A. Klug, TJ Richmond: Comparison of X-ray structures of the nucleosome core particle in two different hydration states. In: J. Mol. Biol. 224, 1992, pp. 253-264, PMID 1548703 .
- ↑ Group TJ Richmond ( Memento of the original from June 3, 2004 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ CA Davey CA, Sargent, K. Luger , AW Maeder, TJ Richmond: Solvent mediated interactions in the structure of the nucleosome core particle at 1.9 Å resolution. In: J. Mol. Biol. 319, No. 5, 2002, pp. 1097-1113, PMID 12079350 .
- ^ TJ Richmond, CA Davey: The structure of DNA in the nucleosome core . In: Nature. 423, 2003, pp. 145-150, PMID 12736678 .
- ^ T. Schalch, S. Duda, DF Sargent, TJ Richmond: X-ray structure of a tetranucleosome and its implications for the chromatin fiber. In: Nature. 436, No. 7047, 2005, pp. 138-141, PMID 16001076 .
literature
- CP Prior, CR Cantor, EM Johnson, VC Littau, VG Allfrey: Reversible changes in nucleosome structure and histone H3 accessibility in transcriptionally active and inactive states of rDNA chromatin. In: Cell . 34, 1983, pp. 1033-1042.
- J. Gòmez-Lira MM Bode, H. Schröter: Nucleosomal particles open as the histone core becomes hyperacetylated. In: Eur. J. Biochem. 130, 1983, pp. 437-445.
- BD Strahl, CD Allis : The language of covalent histone modifications. In: Nature . 403, No. 6765, 2000, pp. 41-45.
- VB Teif, K. Rippe: Predicting nucleosome positions on the DNA: combining intrinsic affinities and remodeler activities . In Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 2009, pp. 5641-5655, doi: 10.1093 / nar / gkp610 .