Histone H1
| H1 histone family, member 0 | ||
|---|---|---|
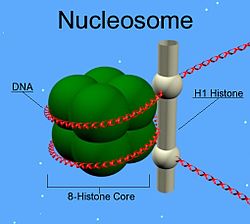
|
||
| Scheme drawing of the nucleosome with histone H1 (rod-shaped) | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 193 amino acids; 20.7 kDa | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | H1.0 ; H1F0; H1FV; H10 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Eukaryotes | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | mouse | |
| Entrez | 3005 | 14958 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000189060 | ENSMUSG00000048769 |
| UniProt | P07305 | P10922 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_005318 | NM_008197 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_005309 | NP_032223 |
| Gene locus | Chr 22: 36.53 - 36.53 Mb | Chr 15: 78.86 - 78.86 Mb |
| PubMed search | 3005 |
14958
|
Histone H1 is an intrinsically disordered protein found in the cell nucleus . It is one of the five main histone proteins of chromatin in eukaryotic cells . In addition to its function as a scaffold for the DNA double strand, it plays a role in transcription . There are at least six different variants of H1, which are designated with H1.1 to H1.5 and H1 0 . Except in simple organisms such as baker's yeast , all variants occur in animals and plants.
biosynthesis
In humans, the gene for variant H1 (0) is on chromosome 22 , all other variants can be found in a group on chromosome 6 . The start methionine is split off from the translation product. The length and the molecular mass of the resulting protein can be read from the table.
| variant | Protein length ( aa ) | Protein mass ( kDa ) | UniProt entry |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 (0) | 193 | 20.7 | P07305 |
| H1.1 | 214 | 21.7 | Q02539 |
| H1.2 | 212 | 21.2 | P16403 |
| H1.3 | 220 | 22.2 | P16402 |
| H1.4 | 218 | 21.7 | P10412 |
| H1.5 | 225 | 22.4 | P16401 |
| H1.T | 206 | 21.9 | P22492 |
Biological function
Histone H1 marks the position where the DNA loops around the histone octamer. In the G1 phase of the cell cycle , the phosphorylation of the protein begins and proceeds to the end of the cell, but is not evenly distributed over the cell nucleus; it is assumed that active (heavily transcribed) genes and a high degree of phosphorylation of H1 are related.
H1 is also poly (ADP-ribosyl) ated. This change, in which 60 to 80 ADP-ribose molecules are attached to H1 in several places (for example by the enzyme PARP-1 ), leads to an opening of the nucleosome and is related to DNA repair .
Other histone proteins
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Alessandro Borgia, Madeleine B. Borgia, Katrine Bugge, Vera M. Kissling, Pétur O. Heidarsson, Catarina B. Fernandes, Andrea Sottini, Andrea Soranno, Karin J. Buholzer, Daniel Nettels, Birthe B. Kragelund, Robert B. Best & Benjamin Schuler: Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex . tape 555 , March 1, 2018, p. 61-66 , doi : 10.1038 / nature25762 .
- ↑ Ronald Berezney, Kwang W. Jeon (Ed.): Structural and Functional Organization of the Nuclear Matrix Academic Press, 1995, ISBN 0123645654 , pp. 214-7.