Oljokma
|
Oljokma Олёкма, Olekma, Өлүөхүмэ (Ölüöchumar) |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 18030400112117200009486 | |
| location | Transbaikalia Region , Amur Oblast , Sakha Republic ( Russia ) | |
| River system | Lena | |
| Drain over | Lena → Arctic Ocean | |
| source | in the Jablonowy Mountains , around 140 km west of Mogotscha 53 ° 44 ′ 42 ″ N , 117 ° 20 ′ 16 ″ E |
|
| muzzle | in the Lena near Olyokminsk Coordinates: 60 ° 22 ′ 27 " N , 120 ° 40 ′ 40" E 60 ° 22 ′ 27 " N , 120 ° 40 ′ 40" E
|
|
| length | 1436 km | |
| Catchment area | 210,000 km² | |
| Discharge at the gauge Srednjaja Oljokma A Eo : 37,300 km² Location: 904 km above the mouth |
MQ 1957/1999 Mq 1957/1999 |
301 m³ / s 8.1 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the gauge Enuka A Eo : 97,600 km² Location: 395 km above the mouth |
MQ 1976/1988 Mq 1976/1988 |
893 m³ / s 9.1 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Kudu-Kjujol A Eo gauge : 115,000 km² Location: 156 km above the mouth |
MQ 1936/1999 Mq 1936/1999 |
1021 m³ / s 8.9 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the gauge near the mouth |
MQ |
1950 m³ / s |
| Left tributaries | Chani , Tumuluur , Tschara | |
| Right tributaries | Tungir , Nyuksha | |
|
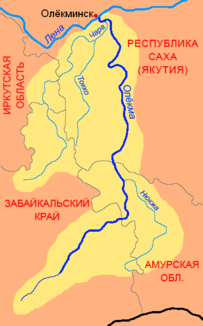
Oljokma with catchment area (yellow) |
||
|
Catchment area of the Oljokma with tributaries |
||
The 1,436 km long Oljokma ( Russian Олёкма , also Olekma ; Yakut Өлүөхүмэ (Ölüöchüm)) is a right tributary of the Lena in Siberia ( Russia , Asia ).
course
The Oljokma rises in the mountain range Oljokminski Stanowik ( Russian Олёкминский Становик ) in the northeastern part of the Jablonowy Mountains in the Transbaikalia region . From there it flows first in a northerly, later increasingly in a northeasterly direction through the sparsely populated high mountain landscape between the western Stanowoi Highlands and the eastern Stanowoi Mountains .
After the confluence of the Tungir , it turns again to the north and crosses the border with Amur Oblast , whose northwest corner it crosses in a widening valley. In Ust-Njukscha which opens Njukscha , their biggest right tributary, one. From here the Baikal-Amur artery runs to the confluence of the Chani in the river's valley.
Shortly before the confluence of the Chani, the Oljokma reaches the Republic of Sakha . Here the river valley narrows again, while the Oljokma flows between the Stanowoy Mountains in the east and the Udokan plateau in the west in a predominantly northerly direction. About 30 km before its mouth it joins at Ust-Tschara with its largest tributary, the Tschara . It leaves the mountains and now flows in the wide valley of the Lena, into which it flows at Oljokminsk .
Hydrology and use
The Oljokma is mainly fed by rain and snow melt water. It has its lowest water level in late winter from February to early April, when it is deeply frozen. The ice breaking, lasting about a week, begins in May and is followed by spring floods that peak in June and provide 37% of annual runoff. In October it will freeze over again.
Almost all of its course, the Oljokma flows in a narrow mountain valley. The narrowness of the valley and the high discharge ensure a high current of 5–5.5 m / s. Only in the last few kilometers, after the confluence of the Tschara and entering the wide valley of the Lena, does this drop to 0.5–1.2 m / s. In the ice-free period and after the floods, the Oljokma is navigable, despite its high current speed and numerous rapids. It is used for water supply and tourism.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Article Oljokma in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ a b Oljokma in the State Water Directory of the Russian Federation (Russian)
- ↑ Oljokma at the Srednjaja Oljokma gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Oljokma at the Enuka gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET
- ↑ a b c Oljokma at the Kudu-Kjujol gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET