Lena (Arctic Ocean)
|
Lena Лена, Өлүөнэ, Ölüöne |
||
|
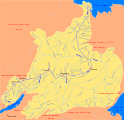
Course of the Lena in eastern Siberia |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 18030900112117500000010 | |
| location | Irkutsk Oblast and Sakha Republic (Yakutia), Siberia , Russia , Asia | |
| River system | Lena | |
| source | in the Baikal Mountains near Lake Baikal 53 ° 55 ′ 58 ″ N , 108 ° 5 ′ 5 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 1465 m | |
| muzzle | within the Lena Delta in the Laptev Sea ( Arctic Ocean ) Coordinates: 72 ° 24 ′ 2 ″ N , 126 ° 41 ′ 31 ″ E 72 ° 24 ′ 2 ″ N , 126 ° 41 ′ 31 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | 1465 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.34 ‰ | |
| length | 4294 km | |
| Catchment area | 2,490,000 km² | |
| Discharge at the Krestovskoe A Eo gauge : 440,000 km² Location: 2,655 km above the mouth |
MQ 1936/1999 Mq 1936/1999 |
4165 m³ / s 9.5 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Tabaga A Eo gauge: 897,000 km² Location: 1527 km above the estuary |
MQ 1936/1999 Mq 1936/1999 |
7007 m³ / s 7.8 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Kusur gauge (Kjussjur) A Eo : 2,430,000 km² Location: 211 km above the mouth |
MQ 1934/2000 Mq 1934/2000 |
16,760 m³ / s 6.9 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Stolb A Eo gauge : 2,460,000 km² Location: 4.7 km above the mouth |
MQ 1976/1994 Mq 1976/1994 |
15,381 m³ / s 6.3 l / (s km²) |
| Left tributaries |
Wiljui (this and others see below ) |
|
| Right tributaries |
Witim , Oljokma , Aldan (these and others see below ) |
|
| Big cities | Yakutsk | |
| Navigable | from Ust-Kut (3,500 km) | |
|
Lena near Yakutsk |
||
The Lena ( Russian Лена ; Yakut Өлүөнэ , Ölüöne ) is a river in Siberia in the Asian part of Russia . It flows into the Laptev Sea , a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean . The Lena is from the source to the Lena Delta km long 4294, on the water-rich Deltaarm Bykowsskaja Protoka is as high as 4400 km in total. It is one of the longest rivers on earth .
course
The Lena rises a little more than five kilometers northwest of Lake Baikal in the Baikal Mountains . Its source is 1465 m above sea level on the western flank of a 2023 m high mountain - in the unpopulated area of the Baikal-Lena nature reserve . In 1997, on the occasion of the 250th birthday of the metropolitan Innokenti of Moscow , who came from this area , a wooden chapel was built in his honor directly at the Lena spring .
Initially, the Lena flows a little north. From roughly the point where it falls below the 1000 m contour line , it runs in a west-south-west direction to Birjulka ( 555 m ) and then westwards to Katschug ( 510 m ). Then the Lena, after changing from the Baikal Mountains to the Lena Angara Plateau , flows a bit to the northwest and north and through Schigalowo ( 410 m ). Before Ust-Kut ( 285 m ) it turns for a bit to the west and before the city turns in an elongated river loop first to the east and then to the northeast. The river is navigable from Ust-Kut . Then at Kirensk ( 248 m ), from where the Lena runs parallel to the Lower Tunguska, which is heading towards the Yenisei and only a few kilometers southeast of this, the Kirenga , which also rises near Lake Baikal, joins . It changes from the Lena-Angara-Plateau to the Central Siberian mountainous region (max. 1701 m ).
After that, the Lena flows in Vitim ( 185 m ) of the light coming from the south Vitim to. A little later, the river at Lensk ( 160 m ) makes an elongated right curve north around the Patom highlands (max. 2148 m ). The Lena turns a bit to the southeast and takes in the Oljokma flowing from the south a little below Oljokminsk ( 125 m ) . From now on it flows to the east-northeast. After taking up the Sinjaja near Sinsk ( 100 m ) and then passing the Lena rocks , it reaches the Central Yakut lowland past Pokrovsk ( 94 m ) to Jakutsk ( 92 m ). After that, the Lena flows first the Aldan, which ultimately comes from the east-southeast, and then, after passing Sangar ( 65 m ) below the former village of Tas-Tumus ( 57 m ), from the west to the Wiljui . In this region the river runs between the Verkhoyansk Mountains (max. 2959 m ; in the east) and the Central Siberian mountainous region (in the west) - mainly in a south-north direction.
A little further to the northwest, coming from the west for its last kilometers, the Linde and after passing Schigansk ( 32 m ) from the same direction the Muna joins the Lena. A little further north-northeast the Molodo flows into Siktjach ( 12.5 m ) . Further northeast, the Lena flows from about Kjussjur ( 6.5 m ) between the northern foothills of the Verkhoyansk Mountains in the east and the Czekanowskibergen (max. 539 m ) (northeast part of the Central Siberian Mountains) in the west.
Finally, the Lena reaches the approximately 45,000 km² Lena Delta , which measures a maximum of 230 km from west to east and up to 150 km from north to south. After flowing through this widely ramified estuary delta , your water reaches the Laptev Sea , a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean .
Lena rocks
Viewed upstream, about 90 km west-southwest of Pokrovsk or 150 km (as the crow flies ) south-west of Yakutsk , the Lena rocks rise in an unpopulated area on the Lena ( ⊙ ). The Cambrian rocks extend a little below the Sinjaja, which flows in from the north, along the south bank of the river, which runs there at a height of about 99 m to 96 m , for about 80 km. They reach a maximum height of around 300 m and their hinterland close to the river a maximum of around 328 m . The rocky landscape is located in the Lenafelsen Nature Park , which was founded in 1995 and is 4850 km² in size, and was designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2012 . To the south, the landscape leads over to the Buotama River , which flows into the Lena a little above Pokrovsk.
Catchment area and tributaries
The catchment area of the Lena corresponds with 2,490,000 km² nearly seven times the area of Germany . The discharge , which varies between 2,800 m³ / s in January and 66,500 m³ / s in June , is mainly due to the melting of the ice between May and June.
The minimum ever measured discharge of the Lena (level Kjussjur on the lower reaches) of 366 m³ / s was recorded on April 27, 1940, the maximum discharge of 220,000 m³ / s on June 4, 1989. In June 1989 the maximum discharge was recorded there of 104,000 m³ / s on a monthly average.

| Tributaries |
|---|
The following list includes larger tributaries of the Lena, viewed downstream: Names of rivers at least 1000 km long are bold, the orographic assignment (l = left-hand side; r = right-hand side), the length in kilometers (km), the location of the mouth, the Lena river kilometers above the confluence with the Laptev Sea and - if known - the catchment area of the tributary in square kilometers (km²):
|
The Lena rocks south of Yakutsk
Lena near Yakutsk
The Lena Delta (NASA Landsat Project)
Ice road over the Lena
Localities
The localities (including former ones ) on the Lena and near the Lena Delta include downstream - with approximate bank heights in meters (m) above sea level (cities in bold , villages that no longer exist in italics , administrative offices of Rajons / Ulussen and urban districts marked with *) :
At the Lena:
|
|
Near the Lena Delta:
- Tiksi * (10 m), coastal and harbor town on the Laptev Sea (about 55 km east of the Lena and a good 20 km south of the eastern part of the Lena Delta)
The villages up to and including Alexejewsk are in the Irkutsk Oblast , all others in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) .
Climate and navigability
The Lena is usually frozen over from October to June of the following year so that it can be used as an ice road . When the ice melts, the Lena becomes a torrent and its water level can rise by 25 meters. Particularly devastating effects are the ice blockages , the consequences of which in May 2001 devastated the city of Lensk and large parts of Yakutsk were flooded. When the river is ice-free, the Lena is navigable from Ust-Kut to its large estuary delta over a length of 3500 km .
literature
- Tatiana Kuschtewskaja : Siberia trip - the Lena. From Baikal to the Arctic Ocean - history and stories along the great Siberian river. Wostok-Verlag , Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-932916-36-6 .
Web links
- Article Lena in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- Hydrographic measuring points in the catchment area of the Lena and neighboring river systems
References and comments
- ↑ a b c d e Lena in the State Water Register of the Russian Federation (Russian) - with tributaries (part 1)
- ↑ Lena at the Krestovskoe gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Lena at the Tabaga gauge - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Lena at the Kusur gauge - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Lena at the Stolb gauge - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Lena River , in: Encyclopedia of the Artic, accessed on August 5, 2017, from books.google.de
- ↑ Topographic map sheet N-49-73 ( scale 1: 100,000), u. a. with Lenaquelle (top left; Лена) near Lake Baikal on the western flank of a 2023 m high mountain in the Baikal Mountains , on vlasenko.net
- ↑ Photo of the chapel
- ↑ Сергей Волков. По Байкалу
- ↑ a b The heights given in the sections “Course” and “Localities” are approximate bank heights, but not heights of the localities / centers.
- ↑ Topographic map, sheet P-52-25,26 (scale 1: 100,000), u. a. with Lena rocks (on the south bank of the Lena; top right), the Lena (Лена) and the Buotama , which flows a little south of it , on vlasenko.net
- ↑ UNESCO World Heritage Center: Lena Pillars Nature Park
- ↑ A. Alekseevskij et al . Лена (PDF) p. 73.
- ↑ Lena in the state register of waters of the Russian Federation (Russian) - with tributaries (part 2)
- ↑ Lena in the state register of waters of the Russian Federation (Russian) - with tributaries (part 3)
- ↑ Lena in the State Water Directory of the Russian Federation (Russian) - with tributaries (part 4)