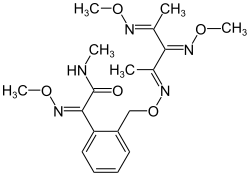
Orysastrobin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Orysastrobin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
(2 E ) -2- (methoxyimino) -2- {2 - [(3 E , 5 E , 6 E ) -5- (methoxyimino) -4,6-dimethyl-2,8-dioxa-3,7- diazanona-3,6-dien-1-yl] phenyl} - N -methylacetamide |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 25 N 5 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish solid with a slightly aromatic odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 391.42 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
96-100 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
225 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Orysastrobin is a chemical compound from the group of amides and methoxyiminoacetamide - strobilurins .
properties
Orysastrobin is a white to yellowish solid with a slightly aromatic odor that is practically insoluble in water.
use
Orysastrobin is used as a fungicide . It is a systemic fungicide with curative and protective properties and a broad spectrum of activity. It disrupts the respiratory processes of the mushrooms (QoI fungicide - Quinone outside inhibitors). It was presented by BASF in 2004, launched in 2007 and marketed against fungal diseases in rice.
Plant protection products containing this active ingredient are not permitted in any EU country or in Switzerland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j data sheet Orysastrobin at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on orysastrobin in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on January 28, 2015.
- ↑ Ulrich Schirmer, Peter Jeschke, Matthias Witschel: Modern Crop Protection Compounds: Herbicides . John Wiley & Sons, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32965-6 , pp. 586,616 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on orysastrobin in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 14, 2016.


