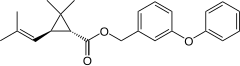
Phenothrin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Phenothrin | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 23 H 26 O 3 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 350.45 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||
| density |
1.061 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||
| boiling point |
> 290 ° C |
|||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.019 hPa (21.4 ° C) |
|||||||||
| solubility | ||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5483 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||
Phenothrin is a mixture of several isomeric chemical compounds from the group of pyrethroids .
Extraction and presentation
Phenothrin can be obtained from chrysanthemum acid and m -phenoxybenzyl alcohol .
use
Phenothrin is used as an insecticide .
Admission
The use of the active ingredient phenothrin in plant protection products is not permitted in the European Union. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted. In Germany, however, numerous biocides (for indoor pest control) with the active ingredient phenothrin are approved.
Stereochemistry
Phenothrin has four stereoisomers (two pairs of enantiomers ) due to the two stereocenters in the cyclopropane ring . The mixture of (1 R ) - cis and (1 R ) - trans isomers is used as an insecticide .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on phenothrin in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 7, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b S. D. Gangolli: The Dictionary of Substances and Their Effects (Dose): OS . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-833-2 , pp. 225 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-422.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 954 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 (PDF) extending the deadline according to Article 8 (2) of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this Directive and the revocation of the approval of plant protection products with these active substances.
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on phenothrin in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved March 3, 2016.
- ↑ Biocide database of the Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (search input → Active ingredient: Phenothrin), accessed on May 12, 2015.
- ↑ Entry on phenothrin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 9, 2020.