Polycaprolactam
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Polycaprolactam | ||||||
| other names |
|
||||||
| CAS number | 25038-54-4 | ||||||
| Monomer | Caprolactam | ||||||
| Molecular formula of the repeating unit | C 6 H 11 NO | ||||||
| Molar mass of the repeating unit | 113.16 g mol −1 | ||||||
| PubChem | 32775 | ||||||
| Type of polymer | |||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Polycaprolactam ( polyamide 6 , PA6 , as a trademark Perlon ) is a polymer from the group of polyamides . This polymer was first synthesized in 1938 by Paul Schlack ( IG Farben ) in order to reproduce the properties of nylon 6,6 without infringing the current production patent.
Manufacturing
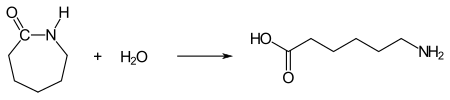
Polyamide 6 is produced by the ring-opening polymerization of ε-caprolactam .
Hydrolytic chain polymerization : ε-aminocaproic acid is required for the start reaction . It is obtained from ε-caprolactam by hydrolytic ring opening. To do this, small amounts of water are added:
ε-aminocaproic acid reacts together with ε-caprolactam to form amide bonds to form polycaprolactam:
The chain polymerization takes place with ring opening at the amino end group of the growing chain. In continuous (VK tube process) or discontinuous processes, the reactions take place in the range from 260 to 280 ° C (VK tube process: 240 ° C). The reaction time is 8 to 10 hours. Remaining monomers are degassed from the melt of the product in a vacuum or extracted from the granulate with water.
Anionic chain polymerisation : This polymerisation is comparatively complicated. For initiation, ε-caprolactam is converted into an anion with alcoholates , primary or secondary amines .
After the addition of caprolactam, an N- acylated caprolactam is formed, the actual active chain end of the chain growth reaction . The growth reaction takes place after:
The slow formation of active chain ends can be accelerated with carboxylic acid chlorides , anhydrides or isocyanates :
The exothermic chain polymerization takes place at 120 to 150 ° C within a few minutes under a nitrogen atmosphere.
Polycondensation : The synthesis of polyamide 6 is also possible via a polycondensation of ε-aminocaproic acid:
use
Polycaprolactam is used as a synthetic fiber under the name Perlon . A wide variety of cast (PA6G) and extruded (PA6E) components are made from polycaprolactam. Due to its toughness and wear resistance, the plastic is used in mechanical engineering for lightly loaded gears and screws , and because of its good sliding properties for highly loaded plain bearings and plates.
In thin-layer and column chromatography it is used as a carrier material ( stationary phase ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Bernd Tieke, Makromolekulare Chemie , 3rd edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2014, p. 117.
- ↑ a b Wolfgang Kaiser, Kunststoffchemie für Ingenieure , 3rd edition, Carl Hanser, Munich, 2011, p. 363.
- ↑ Bernd Tieke, Makromolekulare Chemie , 3rd edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2014, p. 112f.
- ^ Karl-Heinz Lautenschläger, Werner Schröter: Taschenbuch der Chemie , Harri Deutsch Verlag, 2007, Google Books ( page can no longer be accessed , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ↑ EUROPA metal table book.
- ↑ Reinhard Mattisek, Gabriele Steiner, Markus Fischer: Food Analysis . 4th edition. Springer, Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-540-92205-6 .