Progymnosperms
| Progymnosperms | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
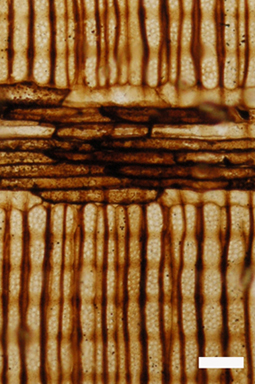
Radial section through the wood of Archaeopteris (bar = 1 mm). |
||||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||||
| Middle Devonian ( Eifelium ) to Lower Mississippian ( Tournaisium ) | ||||||||||||
| 397 to 345 million years | ||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Progymnospermopsida | ||||||||||||
The progymnosperms are an extinct group of vascular plants that mediate in their characteristics between the ferns and the seed plants . Today they are considered to be the group of plants from which the seed plants developed.
features
The progymnosperms mostly had a bushy to tree-shaped growth form. Their branching was pseudomonopodial, but they did not form axillary buds . They had either dichotomous branched units or flat leaves with dichotomous veins.
The organization of the vascular system ranged from a protostele to an eustele with mesaric xylem maturation (from the middle of the primary xylem in both directions). They possessed a bifacial cambium that produced secondary tissue. The secondary xylem is pycnoxylic and consists of tracheids with sacral pits and rays . The wood thus resembled the more recent conifers .
The progymnosperms formed spores. These originated in sporangia that were formed along the adaxial or lateral side of side branches or on modified leaves. There are both isospore and heterospore representatives.
Systematics and evolution
The progymnosperms may have developed from the Trimerophytophyta , the three-ribbed protostele of the early representatives resembles that of the Trimerophytophyta.
The following orders are counted among the progymnosperms :
The progymnosperms are now generally accepted as the precursors of the seed plants. However, there are essentially two theories:
- Rothwell assumes that the seed plants descend monophyletically from an ancestor corresponding to the Aneurophytales.
- Beck assumes that the seed plants originated diphyletically: the seed ferns would therefore descend from the Aneurophytales, Cordaitales and conifers from the Archaopteridales.
Research history
The progymnosperms as spore-forming plants with conifer-like wood were only recognized as such by Charles E. Beck in 1960, when he was able to join the wood and leaves of the plant known today as Archaeopteris, which were previously only known separately .
supporting documents
- Thomas N. Taylor, Edith L. Taylor: The Biology and Evolution of Fossil Plants , pp. 440, 459. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs 1993. ISBN 0-13-651589-4
Individual evidence
- ^ Sarah Matthews: Phylogenetic relationships among seed plants: Persistent questions and the limits of molecular data . American Journal of Botany, Volume 96, 2009, pp. 228-236. doi : 10.3732 / ajb.0800178