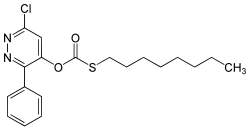
Pyridate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Pyridate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
O - (6-chloro-3-phenylpyridazin-4-yl) - S -octylthiocarbonate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 23 ClN 2 O 2 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 378.92 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.16 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
27 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
220 ° C at 1,013 hPa |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Pyridate is a chemical compound from the phenylpyridazine group .
Extraction and presentation
Pyridate can be obtained by reacting 3-phenyl-4-hydroxy-6-chloropyridazine with S-octyl-thioformyl chloride. The latter is obtained by reacting octyl mercaptan with phosgene .
properties
Pyridate is a colorless solid that is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. The technical product is a brown oily liquid that is sensitive to hydrolysis .
use
Pyridate is used as an active ingredient in crop protection products . It is used as a herbicide against dicotyledonous weeds and is believed to work by inhibiting the Hill reaction .
Admission
The connection has been approved in the Federal Republic of Germany since 1981 and in the GDR since 1984.
Pyridate has been approved as an active ingredient in plant protection products in the European Union since January 2002. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, pesticides (e.g. Lentagran WP) with this active ingredient are approved.
Web links
- Commission Directive 2002/42 / EC of 17 May 2002 amending the annexes to Council Directives 86/362 / EEC, 86/363 / EEC and 90/642 / EEC with regard to the setting of maximum levels for pesticide residues (bentazone and Pyridate) on and in cereals, foods of animal origin and certain products of plant origin, including fruits and vegetables . In: Official Journal of the European Communities . L, No. 134, May 22, 2002, pp. 29-36.
- EU: Review report for the active substance pyridate (PDF; 378 kB), March 22, 2001
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry for CAS no. 55512-33-9 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 4, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Pyridat, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 4, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c G. Matolcsy, M. Nádasy, V. Andriska: Pesticide Chemistry . Elsevier, 1989, ISBN 0-08-087491-6 , pp. 741 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on O- (6-chloro-3-phenylpyridazin-4-yl) S-octyl thiocarbonate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can use the harmonized classification and labeling expand .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide synthesis handbook . 1996, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5 , pp. 525 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Peter Brandt: Active Ingredients in Plant Protection Products ; Approval history and regulations of the Plant Protection Application Ordinance . Springer, Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-0348-0028-0 , pp. 24 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Directive 2001/21 / EC of the Commission of March 5, 2001 amending Annex I of Directive 91/414 / EEC of the Council on the placing of plant protection products on the market and the inclusion of the active substances amitrole, diquat, pyridate and thiabendazole
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Pyridate in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 12, 2016.

