Pyridinedicarboxylic acids
In chemistry, the pyridinedicarboxylic acids form a group of organic compounds that belong to the heterocycles (more precisely: heteroaromatics ). They consist of a pyridine ring that is substituted by two carboxy groups (−COOH). Their different arrangement results in six constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 7 H 5 NO 4 .
They are mostly colorless solids that are difficult to dissolve in water. The melting points are quite high at around 230 ° C, although the dinicotinic acid deviates significantly upwards at 320–325 ° C. Quinolinic acid and cinchomeronic acid decompose by decarboxylation when heated .
The pyridinedicarboxylic acids can generally be prepared from the lutidines by oxidation of the two methyl groups with nitric acid .
The name lutidine is only adopted on the product for the 2,4-isomer : The pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid is called lutidic acid . The Chinolinsäure formed by oxidation of quinoline with potassium permanganate and thus got its name.
Of the picolinic acid ( pyridine-2-carboxylic acid ) is especially forwards the Di picolinic acid ( pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid ), which at the pyridine axisymmetrical in ortho -position two carries carboxyl groups.
Di nicotinic acid ( pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid ) is derived from nicotinic acid ( pyridine-3-carboxylic acid ) and has two carboxy groups on the pyridine, axially symmetrical in the meta position .
| Pyridinedicarboxylic acids | |||||||
| Surname | Pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid | Pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid | Pyridine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid | Pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid | Pyridine-3,4-dicarboxylic acid | Pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid | |
| other names | Quinolinic acid | Lutidic acid | Isocinchomeronic acid | Dipicolinic acid | Cinchomeronic acid | Dinicotinic acid | |
| Structural formula |
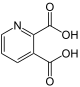
|
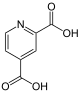
|

|

|

|
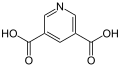
|
|
| CAS number | 89-00-9 | 499-80-9 | 100-26-5 | 499-83-2 | 490-11-9 | 499-81-0 | |
| PubChem | 1066 | 10365 | 7493 | 10367 | 10273 | 10366 | |
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 NO 4 | ||||||
| Molar mass | 167.12 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state | firmly | ||||||
| Brief description | colorless solids | ||||||
| Melting point | 185-190 ° C (dec.) | 242-243 ° C | 236-237 ° C | 224-225 ° C | 266-270 ° C (dec.) | 320-325 ° C | |
| pK s 1 value (25 ° C) | 2.41 | 2.17 | 2.31 | 2.17 | 2.6 | 2.82 | |
| pK s 2 value (25 ° C) | 5.05 | 5.09 | 5.06 | 4.97 | 5.07 | ||
| Solubility in water | 10 g l −1 (20 ° C) | 2.49 g l −1 (25 ° C) | 1.2 g l −1 (25 ° C) | 5 g l −1 (25 ° C) | 2.34 g l −1 (25 ° C) | 1.0 g l −1 (25 ° C) | |
|
GHS labeling |
|
||||||
| H and P phrases | 319-335 | 315-319-335 | 315-319-335 | 315-319-335 | 315-319-335 | 315-319-335 | |
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | ||
| 305 + 351 + 338 |
302 + 352-304 + 340 305 + 351 + 338 |
302 + 352-304 + 340 305 + 351 + 338 |
302 + 352 305 + 351 + 338 |
302 + 352-304 + 340 305 + 351 + 338 |
302 + 352-304 + 340 305 + 351 + 338 |
||
literature
- Hans Meyer, Hans Tropsch: About derivatives of lutidic acid and αγ-diaminopyridine. In: Monatshefte fur Chemie , 35, 1914, pp 189-206, doi : 10.1007 / BF01518123 .
- Hans Meyer, Hans Tropsch: About dinicotinic acid and its degradation to ββ′-diaminopyridine and αα′-diaminopyridine. In: Monatshefte fur Chemie , 35, 1914, pp 207-217, doi : 10.1007 / BF01518124 .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Shinkichi Shimizu, Nanao Watanabe, Toshiaki Kataoka, Takayuki Shoji, Nobuyuki Abe, Sinji Morishita, Hisao Ichimura: "Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives", in: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry , 2002 ( doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a22_3997 ).
- ↑ a b c Quinolinic acid data sheet (PDF) from Merck , accessed December 25, 2018.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet lutidic acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on December 25, 2018.
- ↑ a b c data sheet isocinchomeronic acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 3, 2010.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet dipicolinic acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 3, 2010.
- ↑ a b c Datasheet Cinchomeronic Acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 3, 2010.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet dinicotinic acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on April 3, 2010.
- ^ A b D'Ans-Lax: Pocket book for chemists and physicists , 3rd edition, Volume 1, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg 1967 ( ChemieOnline - pK b and pK s values ).
