Pharyngitis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| J02.- | Acute pharyngitis |
| J31.2 | Chronic pharyngitis |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
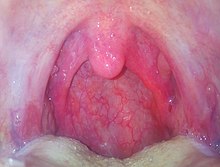
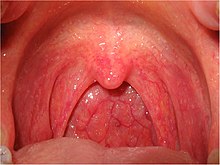
A sore throat ( . Greek - . Anat pharyngitis ; from . Give a wiki φάρυγξ pharynx + -ίτις itis ), and pharyngitis called one is inflammation of the throat mucosa . It occurs in the context of inflammatory processes in the throat and throat area.
etiology
Pharyngitis is one of the most common diseases. For every 1,000 patients who see a doctor, around 200 will have symptoms of pharyngitis. It is one of the most frequent consultation occasions in a general medical practice.
The most common cause of an inflammation of the throat is a viral infection, often as part of a flu-like infection . A distinction must be made between the potentially more threatening bacterial infection.
Non-bacterial origin
The pharyngitis associated with a cold is usually caused by the typical viruses of the respiratory tract ( influenza , parainfluenza or adenoviruses ); Other viruses such as herpes simplex , coxsackie or echo viruses can also be a rare cause of the disease . In addition, viruses, some of which cause systemic diseases , such as Epstein-Barr , cytomegaly , measles , smallpox or rubella viruses, can cause pharyngitis.
Formed by bacteria
Bacteria are less likely to cause pharyngitis. Often β-hemolytic streptococci are involved. Sore throats with accompanying difficulty swallowing can occur, with additional symptoms such as fever, limb pain and headache. The throat and palate and the regional lymph nodes are reddened, swollen and tender on pressure. Children, who are affected far more often than adults, also often complain of nausea and abdominal pain.
Diagnostic criteria for streptococcal pharyngitis are usually given as: fever higher than 38.5 ° C, specks or exudates on the tonsil, petechiae of the uvula and pharyngeal mucosa, enlarged and painful submanidibular lymph nodes, absence of mostly viral signs such as conjunctivitis , cough, Diarrhea.
For complications, see Tonsillitis # Complications
Clinical forms
Pharyngitis atrophicans et sicca
The mucous membrane dries out (lat. Sicca 'dry'). In the neck are Borken visible. In addition, the lymph tissue decreases ( atrophy ). This tissue serves the primary defense against infection, pathogens ingested through the nose or mouth are intercepted and broken down in the lymphatic tissues. In the throat area, the lymphatic organs are called tonsils .
Pharyngitis sicca
The mucous membrane dries out. People who are constantly exposed to dehydrating agents such as: B. smokers and road workers, can show more symptoms.
Lateral cord angina (angina lateralis)
The side strand angina (angina lateralis) is an acute form of pharyngitis caused by bacterial infection that affects those lymphatics in the throat, extending from the upper rear wall of the pharynx downward. Common side effects of the lateral cord angina are earache (due to the proximity to the Eustachian tube ), difficulty swallowing and headache . The lateral cord angina occurs mainly in tonsillectomized patients.
Laryngopharyngitis
The laryngopharyngitis is a combination of Rachenschleimhaut- and laryngitis .
therapy
Viral pharyngitis usually heal completely. Symptomatic therapy with antipyretic or pain relievers may be necessary in the event of a high fever, severe pain and difficulty swallowing. Pharyngitis of bacterial origin, such as the classic lateral cord angina, are treated systemically with antibiotics .
Home remedies
Saliva-producing measures such as B. candy sucking , inhalation or gargling with salt water, whereby the cilia and thus the body's own self-cleaning mechanism of the airways are stimulated. Home remedies for accompanying treatment are locally applicable or inhaled essential oils such as tea tree or eucalyptus oil . These active ingredients can have antibacterial as well as antiviral properties. However, the undiluted use of tea tree oil is dangerous as it can cause lung damage if swallowed.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ According to W. Fink, G. Haidinger: The frequency of health disorders in 10 years of general practice. In: ZFA - Journal for General Medicine. 83, 2007, pp. 102-108, doi : 10.1055 / s-2007-968157 . Quoted from "What family doctors mainly deal with", MMW-Fortschr. Med. No. 16/2007 (149th year).
- ^ Renz-Polster, Herbert, Krautzig, Steffen, Braun, Jörg: Basic textbook internal medicine compactly tangible, understandable, Urban and Fischer Verlag, Munich, 2004, 3rd edition.
- ↑ Aliki Nassoufis: Column: Health tip: Sore throat? Scarf away! In: welt.de . October 13, 2008, accessed October 7, 2018 .
- ↑ Tea Tree Oil Eliminates Herpes Viruses, Pharmazeutische-Zeitung online 2001 , accessed March 2, 2014.
- ↑ Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), Use of undiluted tea tree oil as a cosmetic product , accessed June 7, 2014.