Remifentanil
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
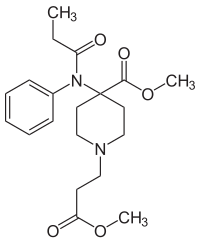
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Remifentanil | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Methyl 3- {4-methoxycarbonyl-4 - [(1-oxopropyl) phenyl-amino] -1-piperidine} propanoate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 28 N 2 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Opioid analgesic |
|||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 376.45 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
212-214 ° C (hydrochloride) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Remifentanil is an extremely short-acting, highly potent opioid that is used in particular in anesthesia .
pharmacology
Remifentanil is a pure µ-agonist with a relative potency of 200 (to the reference substance morphine ). The spectrum of activity includes the typical opioid effects such as analgesia , miosis and particularly pronounced sedation and respiratory depression , which is why safe handling of this opioid is only guaranteed under clinical conditions. The degradation takes place independently of the organ by unspecific esterases , so a dose adjustment is not necessary in the case of impaired liver or kidney function. It is degraded to 98% by hydrolysis of the ester bond and to 2% by N -dealkylation; the resulting compounds practically no longer have an opioid effect. The half-life of remifentanil is reported to be six minutes or less.
application areas
Remifentanil is mainly used in total intravenous anesthesia ( TIVA ), mostly in combination with propofol . Due to the short terminal elimination half-life of only 12–30 minutes, remifentanil is usually used continuously e.g. B. supplied via a syringe pump . There is therefore hardly any accumulation in adipose tissue; Effect overhangs are very unlikely. The very good controllability made possible by this has contributed to its widespread use, especially in outpatient anesthesia . In addition, it can be used as a short-acting monoanalgesic with less painful measures (e.g. lithotripsy ) under appropriate supervision . However, the short and constant context-sensitive half-life of the substance also means that there is no longer any analgesia shortly after the administration has ended and, depending on the pain intensity, another analgesic must be given.
particularities
The dosage of Remifentanil must be adapted to the age. Significant drops in blood pressure and heart rate have been described, especially with higher doses and in less painful phases of surgery.
In a study with sixty intensive care patients, no superiority of remifentanil versus fentanyl with regard to pain reduction, treatment and ventilation duration could be proven. According to the information for professionals, there are no studies available for Remifentanil when used for more than three days. As a result, use over this period is not recommended.
Trade names
Remifentanil has been used in Germany, Austria and Switzerland a. a. sold under the trade name Ultiva by Glaxo Smith Kline . The patent expired on September 10, 2017 and enabled generics to enter the market. B. Fresenius Kabi are also offered.
Legal status in Germany
Remifentanil is a marketable and prescription narcotic drug in the Federal Republic of Germany due to its listing in Appendix 3 BtMG. Handling it without permission or prescription is generally a criminal offense. Further information can be found in the main article Narcotics Law in Germany .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on remifentanil. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 25, 2014.
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of [No public or meaningful name is available] in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on July 11, 2020, is reproduced from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine for specialist care. Springer-Verlag, 2014, ISBN 978-3-642-28291-1 , p. 155 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ http://anesthesiology.pubs.asahq.org/Article.aspx?articleid=2323543
- ↑ Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine in cardiac, thoracic and vascular surgery. (1st edition 1986) 5th edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York et al. 1999, ISBN 3-540-65024-5 , p. 32 f .; here: p. 33.
- ↑ C. Spies, M. Macguill, A. Heymann, C. Ganea, D. Krahne: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study comparing remifentanil with fentanyl in mechanically ventilated patients. In: Intensive Care Med. 37 (3), Mar 2011, pp. 469-476. doi: 10.1007 / s00134-010-2100-5 . PMID 21165734
- ↑ Specialist information Remifentanil on the Carinopharm website; available as pdf ( memento of the original dated November 7, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. ; last accessed on December 12, 2015.
- ↑ Michael Heck, Michael Fresenius: Repetitorium Anaesthesiologie. Preparation for the anesthesiological specialist examination and the European diploma in anesthesiology. 3rd, completely revised edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York et al. 2001, ISBN 3-540-67331-8 , p. 804.