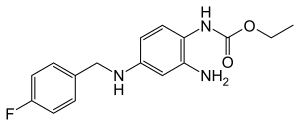
Retigabine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Retigabine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 18 FN 3 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
KCNQ2 / 3-NC contact |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 303 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Retigabine is a drug with an antispasmodic effect. In March 2011, retigabine was approved throughout the EU under the trade name Trobalt as an add -on therapy for focal seizures in patients with epilepsy in whom other combinations with other suitable drugs were ineffective or not tolerated.
Trobalt was developed in collaboration between the US pharmaceutical company Valeant Pharmaceuticals International and the British pharmaceutical company GlaxoSmithKline . In 2017 it was withdrawn from the market worldwide
pharmacology
properties
Retigabine has a plasma protein binding of 80%. The plasma half-life is 7.4–9.2 hours, the dihydrochloride is used medicinally. The application is carried out orally. Structurally and functionally, it is closely related to the pain reliever flupirtine, which has not been approved since 2018 due to its hepatotoxic potential .
Mechanism of action
Retigabine causes a highly specific activation of the voltage-dependent potassium channels KCNQ2 / KCNQ3 of the M-type in the brain . Subunits of these channels are responsible for the selective control of the excitability of nerve cells . Activation has an anticonvulsant effect as well as against Parkinson's disease and is neuroprotective . If these potassium channels are mutated, impulse transmission in the brain is disturbed. Retigabine opens these channels and thus stabilizes the depolarized nerve cells.
At GABA A receptor types with delta subunits , it enhances the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA , which also contributes to the anticonvulsant effect.
Side effects
In American post-marketing studies, it was found that retigabine caused a blue discoloration of the skin in 6.3% of the participants in the former approval study after long-term use, mainly around the lips and nails. It is currently unknown whether the discoloration is reversible. The affected patients had taken the drug for an average of more than four years. In addition, it can lead to a pigmentation disorder of the retina, which can also lead to a possibly irreversible reduction in visual acuity.
Approval as a drug
In March 2011, retigabine was approved across the EU under the trade name Trobalt . In Germany, the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) came to the conclusion in May 2012 that retigabine has no additional benefit compared to the comparator substances lamotrigine and topiramate , despite its clear effect in some of the patients . The company GlaxoSmithKline then announced that it would initially take the drug off the market in Germany. This took place worldwide in 2017.
Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)
Retigabine is used orally and has an absorption that can be influenced by high-fat food, with generally low bioavailability. Together with its fast kinetics, this makes it difficult to set stable effective levels. Avoid overdosing due to side effects. Retigabine must therefore be gradually increased individually for each patient. Carrying out a TDM is therefore recommended.
literature
- GL Plosker, LJ Scott: Retigabine. In partial seizures. CNS drug review 20, 601-608 (2006).
- G. Blackburn-Munro, W. Dalby-Brown, NR Mirza, JD Mikkelsen, RE Blackburn-Munro: Retigabine. Chemical synthesis to clinical application. CNS drug review 11, 1-20 (2005).
- Use of Retigabine for treating neuropathic pain . Patent entry WO / 2001/022953 at Wipo.int.
- C. Runfeldt, R. Bartsch, A. Rostock, C. Tober, R. Dost: Use of Retigabin for treating neuropathic pain. WIPO, 1-7 (2001).
- G. Dannhard, W. Kiefer: New anti-epileptic drugs in development. Substances with new mechanisms of action. In: Pharmazie in our time 36/4, pp. 306-310 (2007).
- TV Wuttke: Characterization of the molecular mechanism of action of the new anticonvulsant retigabine on the KCNQ2 potassium channel. (Abstract) Dissertation University of Ulm, 2006.
- New drugs: Trobalt® (retigabine) Information from the drug commission of the German medical profession, May 30, 2011
Individual evidence
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of carbamic acid, N- [2-amino-4 - [[(4-fluorophenyl) methyl] amino] phenyl] -, ethyl ester in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA ) is shown, which is derived from a self-classification by the distributor ), accessed on July 11, 2020.
- ↑ https://www.deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de/news/artikel/2017/05/03/endgueltiges-aus-fuer-antiepileptikum-trobalt
- ↑ M. Treven, X. Koenig, E. Assadpour, E. Gantumur, C. Meyer, K. Hilber, S. Boehm, H. Kubista: The anticonvulsant retigabine is a subtype selective modulator of GABAA receptors. In: Epilepsia. Volume 56, number 4, April 2015, pp. 647-657, doi : 10.1111 / epi.12950 , PMID 25779225 , PMC 4949651 (free full text).
- ↑ Potiga (Ezogabine): Drug Safety Communication - Linked To Retinal Abnormalities And Blue Skin Discoloration. FDA notification dated April 26, 2013.
- ^ Frank A. Miltner: Epilepsy: Drug with an innovative mechanism of action (retigabine) classified as "no additional benefit". German Society for Neurology, press release from June 4, 2012 from Informationsdienst Wissenschaft (idw-online.de), accessed on August 24, 2015.
- ↑ Analysis spectrum of retigabine. ( Memento of the original from December 10, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. labor-lademannbogen.de, as of April 26, 2013.