Rescue diving
Rescue diving (also emergency diving or rescue diving ) is diving in aid organizations. Diving tasks include rescuing people, rescuing corpses, animals, vehicles and other goods from the water and performing technical measures under water.
In Germany there are civil service divers at the water rescue service , the German Life Rescue Society (DLRG), the Arbeiter-Samariter-Bund (ASB), the fire brigade ( fire service divers ), the THW and the police (rescuing people not primary task), in Austria among other things in the fire brigade , the Austrian water rescue and in the Austrian rescue service and in Switzerland especially in the Swiss life saving society .
The smallest unit that can be deployed is a diving squad . Diving under often difficult conditions places high physical and psychological demands on the emergency services. Often times you have to work under great time pressure and in many waters there are also extremely poor visibility. The divers therefore have to complete a one to two year training course followed by a theoretical and practical test. Furthermore, active rescue divers must have completed a certain number of dives annually in order to receive their rescue diving license . In addition, the tested operational divers must attend an annual training course.
In Germany, in order to remain rescue divers within the meaning of DGUV -Rule DGUV-R 105-002, at least ten dives per year must be carried out under operational conditions, whereby these dives must last at least 300 minutes in total. In addition, divers there must have their health checked by a doctor once a year according to G31 (overpressure) .
Line pull mark
Leash signals are used for communication between signal man and rescue diver or, in the case of modern full face masks, a wire radio device or ultrasonic radio device. The binding line pull marks are specified in DGUV rule 105-002 in appendix 5.
| Linen sign | from the diver | from the leash guide |
|---|---|---|
| x |
Distress signal I'm in need! |
Dive out the emergency signal immediately! |
| xx | - | To the left |
| xxx | - | To the right |
| xxxx | I'm diving out | Diving out |
| xxxxx | Everything OK! | Everything OK? |
- Legend
- x stands for a pull on the line.
Additional line pull marks can be agreed between the diver and the signalman.
For example, the following line signs originating from former versions of the fire service regulation 8 (FwDV 8) diving (e.g. still contained in the 1986 version) can be agreed:
| Linen sign | from the diver | from the leash guide |
|---|---|---|
| xx - x | - | Forward |
| xx - xx | - | Back |
| xx - xxx | - | Search on the spot |
| xxx - xxx | Need support! | - |
The use of the single train as a partial signal is misleading in the context of the emergency signal.
education
At the DLRG
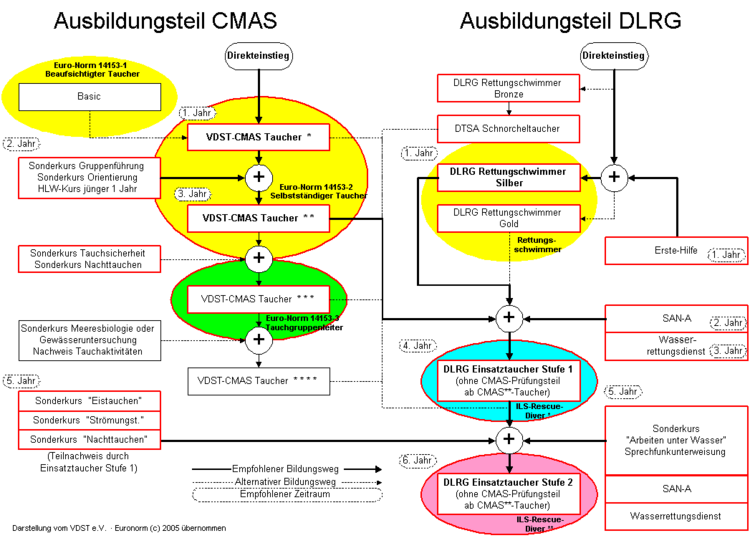
The DLRG regulates the requirements, the training and the examination of the divers in the examination regulations 6.
The scheme was generated from the examination regulations of the VDST and the DLRG (as of 2006).
At the water watch
The training to become a rescue diver is regulated by the diving training / examination regulations (APV-T) and Appendix 3 of GUV rule 2101. A diving candidate must complete a one to two year training course with a final theoretical and practical examination. To begin training as a rescue diver, the following requirements must be met:
- Completion of the 15th year of life before the start of training
- In the case of minors, written permission from their legal guardians for training
- Membership of the water watch
- German lifeguard badge silver or gold (not older than 2 years)
- First aid training (not older than 2 years) or first aid training (not older than 1 year)
- Medical training A, B and C (qualification: water rescuer in the water rescue service)
- Health suitability according to G 31 (overpressure)
Course of training
- 20 UE training on land
- 20 units of training in the swimming pool
- Training with ABC equipment
- Training with diving equipment
- 30 units of training in open water
1 teaching unit (TU) corresponds to 45 minutes
In the THW
In the German THW , rescue divers are trained and deployed in accordance with THW service regulation 8, the content of which is closely based on fire service regulation 8. The first task of rescue divers is the rescue of people , which, based on the usage of the term rescue in the dictionary for civil protection and disaster relief , also includes rescue in the sense of the fire service regulations.
Regulations for the operational diver
Statutory accident insurance regulations
- GUV - V A1 General regulations
- GUV - R 2101 Diving with light diving equipment in rescue companies
- BGV - C 23 accident prevention regulation diving
On May 1, 2014, the DGUV changed the system for naming regulations:
- GUV - V A1 → DGUV regulation 1
- GUV - R 2101 → DGUV rule 105-002
- BGV - C 23 → DGUV regulation 40
Laws
- Pressure Equipment Ordinance
- Industrial Safety Ordinance
- Product Liability Act
- WHG Water Resources Act
- ADR / GGVSE European Agreement on the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road / Dangerous Goods Ordinance by Road and Rail
Norms
- EN 250/2000 Autonomous light diving equipment with compressed air
- EN 13949 Autonomous light diving equipment with nitrox gas mixture
- EN 12021 compressed air for breathing apparatus
- EN 12628 Combined buoyancy and rescue equipment
- EN 1809 buoyancy compensator (jacket)
- EN 14225 part 1 wet suits
- EN 14225 part 2 dry suits
- EN 1972 diving accessories; snorkel
- EN 13319 diving accessories; Depth gauge
- EN 8306 diving watches
See also
literature
- Manuel Döhla: SEGmente 13: Units and management organization in diving operations. Stumpf + Kossendey, Edewecht, ISBN 978-3-943174-49-6 .
Web links
- Information on rescue diving training from the water rescue service
- Diving in the DLRG
- Information on rescue diving training of the ÖWR
- oerd.or.at
Individual evidence
- ↑ Examination regulations on dlrg.de (PDF; 573 kB).
- ↑ DGUV rule 105-002 (previously GUV-R 2101, previously GUV 10.7) Rules for safety and health protection ( memento of the original from September 6, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 301 kB)
- ↑ The complete transfer list is under DGUV transfer list ( Memento of the original from August 21, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF).