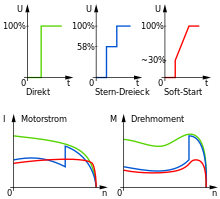Soft start
As a soft start (Engl. Soft Start ) measures, performance limitation when switching an electrical appliance usually a larger power supply or electric motor called.
On the one hand, this reduces the inrush current of the device (inrush current limitation); with large loads, this also prevents a circuit breaker from responding or a severe voltage drop in the mains voltage. On the other hand, the mechanical components driven by motors are protected from excessive torques and accelerations. Especially with hand-held devices (e.g. angle grinders), the reduction of the reaction forces during start-up is also important.
Inrush current limitation
With resistance
A limitation can by one in series with the consumer switched resistance can be achieved. If this is an ohmic resistor , it may only be in the power line when it is switched on and must later be bridged by a relay , a thyristor or a triac during normal operation . Inrush current limiters of this kind are also referred to as “voltage-controlled” because the voltage is bridged shortly after the voltage is switched on.
The advantage of this variant compared to the inrush current limitation with NTC thermistors is that the current is limited even when the device is switched on again shortly after it is switched off. However, the resistor can overheat if it is switched on and off frequently in quick succession or if the bridging function is defective or missing, and in the worst case it can cause a fire. For this reason, countermeasures should be taken, such as the use of flame-retardant resistors, those with a built-in safety function (e.g. fusible wire resistor) or a separate fuse in the resistance circuit. In addition, such inrush current limiters are not short-circuit proof during switch-on.
On-off switches with a pneumatically or hydraulically delayed second switching path are a very rare type of resistance bridging. The second, delayed closing switch bridges the resistor used to limit the inrush current during operation. These switches only work if they are switched off themselves, but not if the device is otherwise disconnected from the mains and switched on again. This principle can be found on larger angle grinders, which delay the bridging contact for the starting resistance with a highly viscous oil / grease filling.
With thermistor (NTC)
In power supplies usually one is called inrush thermistor in (NTC resistor) used series is switched to the consumer, needs to be bridged but not necessarily. Due to its high resistance when cold, it limits the current after switching on. Later it heats up due to the flow of current, reduces its resistance and then causes only minor losses in order to maintain its own temperature.
After switching off the device, you have to wait a certain time (often several minutes) until the thermistor has cooled down again, otherwise the current is no longer sufficiently limited when you switch it on again. This time can be shortened considerably if the NTC is bridged with a relay a few milliseconds after switching on, as shown in the picture.
Overhead projectors are often switched on and off several times a day, which puts a heavy load on the current-limiting NTC, so that it often fails after a relatively short time. You can extend the time until the device fails by providing two NTCs connected in parallel, because if one NTC fails, the second takes over its function.
NTC inrush current limiters are usually built into the device because the NTC type must be matched to the load. Less often, however, they can also have their own housing in the form of an adapter plug.
NTC resistors or NTC resistors intended to limit the inrush current are specified by their maximum operating current (rated current), the cold resistance and the switch-on characteristics of the connected consumer. For this purpose, the manufacturer specifies the nominal current and the cold resistance as well as the maximum current integral I 2 · t or the maximum permissible value of the subsequent charging or filter capacitor. The cold resistance (usually specified as R 25 for 25 ° C) determines the maximum inrush current when the component has cooled down. Typical resistance values are 5 ... 25 ohms, so that circuit breakers just do not respond.
With semiconductors
With leading edge
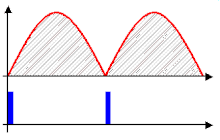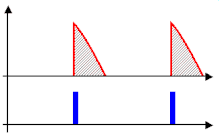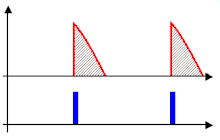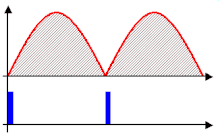
Phase control thyristors or triac are often used to limit the inrush current of inductive loads (including transformers, motors for angle grinders and vacuum cleaners ) . These modules gradually control the current flow angle in the form of a ramp to the full value. Often they can also serve as power controllers.
A variant for limiting the inrush currents of transformers are electronic inrush current limiters or transformer switching relays . With them the thyristors are bridged with a relay contact after switching on. Such ballasts do not heat up and avoid the inrush current even after repeated switching on and also handle failures of only one network half-cycle, which would otherwise drive the connected transformer into saturation when the mains is restored.
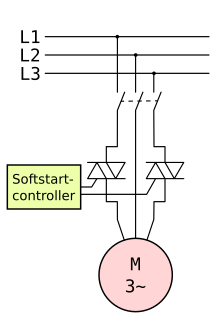
A basic distinction is made between two-phase and three-phase soft starters for motors. The two-phase soft starters are cheaper to buy than the three-phase soft starters, but have the disadvantage that they generate voltage asymmetries through the two switched phases and thus cause the DC voltage components in the rotor to produce elliptical rotating fields. This is expressed by an "out of round" approach that is clearly audible. This starting procedure is also not advantageous for the bearings and gears. Some manufacturers of these two-phase soft starters try to compensate for these disadvantages with special control methods. However, the better technique is three-phase switching. In addition, a distinction is made between the IN-LINE circuit and the IN-DELTA circuit for three-phase soft starters. IN-LINE means that the soft start switches between the motor protection switch and the motor. The soft start must be designed for the conductor current, for which 3 conductors + PE are required. IN-DELTA means that the soft start is switched into the three winding phases of the motor. 6 conductors + PE are required from the motor to the control cabinet. The advantage of the DELTA circuit, however, is that the phase current is lower by a factor of root 3 (phase current = 58% conductor current), which results in smaller sizes of the soft starters and lower power loss.
Inrush current limitation and soft start for power supplies
In the case of power supplies , a high current initially flows after switching on because the intermediate circuit capacitors are charged first. Also, power transformers , especially toroidal transformers can have a high inrush cause.
Possible measures against the high inrush current in switching power supplies that switch on the primary side and also in large power transformers are inrush current limiters with resistance or NTC thermistors , as described above. Transformer switching relays are particularly suitable for smoothly switching on transformers. In a special design, switched-mode power supplies can also be switched on gently.
The control of switched-mode power supplies usually increases the output voltage slowly (soft start) so that the inrush current is not increased by the load and the output capacitors.
Inrush current limiters with phase control are only used in specially adapted special designs for primarily switched-mode power supplies, because a switch-mode power supply represents a capacitive load that causes high current peaks if the phase control is not adapted.
Switching power supplies with active electronic power factor correction (PFC) also have the problem of a high inrush current, which at the moment of switch-on flows through the inductor and the diode of the boost converter into the charging capacitor of the DC intermediate rail until it is charged to the peak voltage . Since the choke has a low inductance because it is only operated at high frequencies for the PFC, it limits the current only slightly. Therefore, such switched-mode power supplies usually also have an NTC to limit the inrush current. Power supplies with passive power factor correction, on the other hand, have a choke with a higher inductance in the input (for mains frequency). This often limits the inrush current sufficiently.
Soft start of motors
A universal motor or series motor accelerates with high power without a soft start and delivers the highest torque - the holding torque - from standstill. The starting current is high, but it immediately adds to the torque. A start without a soft start rarely leads to a fuse responding . However, soft start is also used in these motors to reduce the current load on switches or to reduce the torque on the drive shaft or on other transmission elements - e.g. B. a clutch - to limit, so that they are protected from mechanical overload. Soft start can also play a decisive role for safety reasons, v. a. For better and safer handling of electrical hand-held devices equipped with such motors (drill, angle grinder, hand-held circular saw), devices for transporting people (carousel and Ferris wheel at the fair) and objects (baggage belt at the train station, from which jerky starting, etc. . Luggage would fall down).
For motors for single-phase alternating current , e.g. B. large angle grinders and circular saws , where a high current flows for a relatively long time until the motor has accelerated the grinding wheel or the saw blade to the nominal speed, inrush current limiters are often required; In this context, these are also referred to as inrush current limiters and can be built into the device or have their own housing as an adapter between the socket and the power plug of the device.
Asynchronous motors cause very high inrush currents with initially low torque. Shortly before reaching the nominal speed, however, the torque increases very sharply. In some cases, such as conveyor belts , cranes and elevator systems , a smooth start and stop of the motor is desired in order to reduce accelerations which e.g. B. could lead to vibrations or falling of transported goods. Frequency converters are often used here.
Soft start circuits
Asynchronous motors are often started by star-delta connections or with frequency converters . The KUSA circuit , the soft starters described below or, in the case of high outputs, slip ring motors , for example historically with a liquid starter, are used for the soft start .
Vacuum cleaners often have a soft start circuit in the form of a triac actuator with "soft start" behavior. This can be designed with or without adjustable power - the same assembly is often used, even if there is no power controller on the device.
In the case of hand-held devices, soft start is often achieved with a "throttle" (a triac actuator housed in the handle switch ) or by a soft start circuit that also works with a triac without a power setting.
Soft starters
There are electronic soft starters for large asynchronous motors . Such a soft starter reduces the voltage when switched on by means of phase control and increases it slowly up to full mains voltage. However, with asynchronous motors the torque of the motor decreases quadratically with a lower voltage , and the torque is also low at very low speed. This is why such a soft start is only possible in a no-load condition or with a low load. When full voltage is reached, the electronics of some soft starters are bridged by relays or contactors in order to reduce the power loss . Soft starters are used, for example, for large fans and machines in industry. Starting with nominal load is also possible here.
Some soft starters also have a function for slowly reducing the motor voltage when switching off (soft stop) or are combined with electronic braking devices to bring the motor to a standstill quickly. Devices are also available on the market that can generate a braking torque while the motor is running down - this significantly reduces the run-down time of the load (e.g. when braking large fans).
Soft starters are often also offered with an overload relay function.
Soft starters often replace the previously widespread star-delta switches , in which the motor voltage is increased in two stages.
frequency converter
Another method of achieving a soft start with asynchronous motors is to use a frequency converter with which the speed can be slowly increased to the full value with a programmable ramp function. In contrast to reducing the voltage with a soft starter, the motor has a high torque even at low speeds when operated with a frequency converter. Therefore, the speed can be increased very slowly if necessary, z. B. to cope with large moments of inertia. The torque may briefly have higher values than in nominal operation, so that start-up is also possible under full load. This is important at the start u. a. of compressors, if they have to start against the still existing pressure.
Another advantage of frequency converters is the possibility of being able to vary the speed of the motor during operation and, depending on the requirements, to reduce the speed slowly or to brake the motor in a controlled manner when switching off.
In addition, modern frequency converters are often equipped with a power factor correction; In contrast to phase angle controls, there are hardly any harmonics in the power grid.
Electronic frequency converters are much more complex and therefore more expensive than soft starters with phase control, but are increasingly used because of their advantages.
literature
- Wolfgang E. Schmidt: Learning situations energy and building technology for electronics technicians and electrical installers. 1st edition, Verlag Handwerk und Technik GmbH, Hamburg 2005, ISBN 3-582-03671-5 .
- Gert Hagmann: Power electronics. 3rd edition, AULA-Verlag GmbH, Wiebelsheim 2006, ISBN 978-3-89104-700-2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Data sheet Siemens Sirius SA devices. Retrieved July 24, 2017 .