Scandium oxide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Sc 3+ __ O 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system | ||||||||||||||||
| Space group |
Ia 3 (No. 206) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 985 pm |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Scandium oxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Sc 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 137.91 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
3.86 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
2485 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.9943 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Scandium oxide (Sc 2 O 3 ) is the combustion product of elemental scandium in air. It arises from the oxidation of scandium to Sc 3+ at 800 ° C or from the annealing of scandium salts . It is a white powder with a melting point of 2485 ° C.
properties
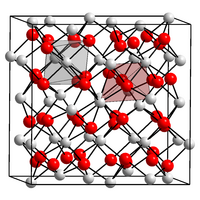
Scandium oxide crystallizes in the cubic crystal system in space group Ia 3 (space group no. 206) with the lattice parameter a = 985 pm and 16 formula units per unit cell . In the crystal structure , the Sc 3+ cations are coordinated six times by oxygen in the form of octahedra . Structurally Sc corresponding 2 O 3 so that the lanthanoid - oxides of the C type, which also in the structures of lanthanide sesquioxides the general shape of Ln 2 O 3 for Ln = Dy - Lu and Y occurs.
use
Scandium oxide is used for the doping of magnetic storage in the computer industry. The magnetization reversal is accelerated and the computing power is increased. It is the starting product for the production of the metal scandium. It is converted into scandium (III) fluoride (ScF 3 ) and then reduced to the metal using calcium .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on scandium oxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on December 12, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Index of Refraction of Inorganic Crystals, pp. 10-248.
- ^ Osvald Knop, Jean M. Hartley: Refinement of the crystal structure of scandium oxide . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 46 (8), 1968, pp. 1446-1450, doi : 10.1139 / v68-236 .