Secologist
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
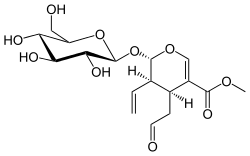
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Secologist | |||||||||
| other names |
Loniceroside |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 24 O 10 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 388.37 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
94-96 ° C |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Secologanin is a glucoside and a secoiridoid that play a central role in the biosynthesis of many alkaloids . It forms a colorless oil. The monoterpene glycoside is a key component in the synthesis of most indole alkaloids , as well as the cinchona , ipecac and pyrroloquinoline alkaloids , as well as simple monoterpene alkaloids. Almost a quarter of all alkaloids formed in living organisms are built up from it.
biosynthesis
The secologanin biosynthesis originally begins with geraniol through several intermediate steps. Secologanin itself is then either formed from the iridoid loganin . For this purpose, the cyclopentane ring of the loganin between the C 7 and C 8 atoms is split oxidatively . This reaction is catalysed by a secologanin synthase ( EC 1.3.3.9 ), a cytochrome P450 enzyme, for which NADPH and oxygen are required.
In Catharanthus roseus (pink Catharanthe), secologanin is synthesized from loganate, the anion of loganic acid. This catalyzes a methyl transferase ( EC 2.1.1.50 ), during the reaction S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) is consumed.
Secologanin can - catalyzed by strictosidine synthase - react further to form strictosidine .
Web links
- Secologanin biosynthesis , at: School of Biological & Chemical Sciences at Queen Mary, University of London .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Secologanin at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 14, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on Secoiridoide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 14, 2017.
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to Loganin : CAS number: 18524-94-2, EC number: 242-398-0, ECHA InfoCard: 100.038.529 , PubChem : 87691 , ChemSpider : 79111 , Wikidata : Q15426222 .
- ↑ Horst Rimpler (Ed.): Biogenic medicinal substances . 2nd edition, Deutscher Apotheker Verlag, Stuttgart 1999, ISBN 3-7692-2413-2 , p. 296.
- ↑ Hirobumi Yamamoto, Nobuyuki Katano, Ayaka Ooi, Kenichiro Inoue: Secologanin synthase which catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of loganin into secologanin is a cytochrome P450. In: Phytochemistry . 53, No. 1, 2000, pp. 7-12, doi : 10.1016 / S0031-9422 (99) 00471-9 , PMID 10656401 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to loganic acid : CAS number: 22255-40-9, EC number: 244-875-9, ECHA InfoCard: 100.040.781 , PubChem : 89640 , ChemSpider : 80905 , Wikidata : Q19597767 .
- ↑ Jun Murata, Jonathon Roepke, Heather Gordon, Vincenzo De Luca: The leaf epidermome of Catharanthus roseus reveals its biochemical specialization. In: The Plant Cell. 20, No. 3, 2008, pp. 524-542, doi : 10.1105 / tpc.107.056630 , PMID 18326827 , PMC 2329939 (free full text, PDF).
- ↑ Horst Rimpler (Ed.): Biogenic medicinal substances . 2nd edition, Deutscher Apotheker Verlag, Stuttgart 1999, ISBN 3-7692-2413-2 , p. 307.
