Strictosidine synthase
| Strictosidine synthase ( Rauvolfia serpentina ) | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Belt model according to PDB 2FP9 | ||
|
Existing structural data: s. UniProt |
||
| Mass / length primary structure | 322 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Identifier | ||
| External IDs |
|
|
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 4.3.3.2 , lyase | |
| Response type | Pictet-Spengler condensation | |
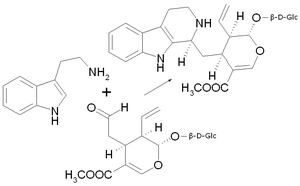
| Substrate | Tryptamine and secologanin | |
| Products | Strictosidine and H 2 O | |
Strictosidine synthase is a plant enzyme which the Mannich-type condensation of tryptamine and Secologanin according strictosidine catalyzed . This is an important step in the biosynthesis of the indole alkaloids . The enzyme is located in the vacuoles of the roots.
The next step in the anabolic metabolic pathway of strictosidine is deglycolysis by strictosidine glucosidase to yield cathenamine.
Strictosidine synthase has a molecular mass of about 34 kDa and was first isolated in 1979 from cell cultures of Catharanthus roseus and described by Johannes Treimer and Meinhart Zenk at the Ruhr University in Bochum . Since then, the enzyme has also been isolated from other plants of the dog venom family and the enzyme from the species Catharanthus roseus , Rauvolfia serpentina and Ophiorrhiza pumila has been cloned . Although strictosidine synthase has a high substrate specificity and a high substrate affinity ( K M of 2.3 m M for tryptamine and 3.4 m M for secologanin), it also tolerates differently substituted tryptophan and secologanin as substrates.
The enzyme belongs to the class of amine lyases ( EC 4.3), which synthesize carbon-nitrogen bonds. The enzyme plays in the synthesis of indole alkaloids an important role because Strictosidine the precursor of about 3000 different indole - terpene - alkaloids is, including the two major cancer drugs vincristine and vinblastine , the antimalarial drug quinine , the antihypertensives reserpine and antiarrhythmic Ajmalin .
In 2006, researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz succeeded in elucidating the structure of the enzyme from Rauvolfia serpentina . The researchers solved both the structure of the native plant protein and the structure of a mutated protein. Structurally, the enzyme is a beta propeller with a six-fold pseudo-symmetry axis. The six subunits are made up of four anti-parallel beta sheets . The protein crystallizes as a dimer, but is active as a monomer.
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt P68175
- ^ McCoy E, Galan MC, O'Connor SE: Substrate specificity of strictosidine synthase . In: Bioorg Med Chem Lett. . 16 (9), 2006, pp. 2475-8. PMID 16481164 .
- ↑ a b c Treimer JF, Zenk MH: Purification and properties of strictosidine synthase, the key enzyme in indole alkaloid formation . In: Eur J Biochem . 101, 1979, pp. 225-33. doi : 10.1111 / j.1432-1033.1979.tb04235.x . PMID 510306 .
- ↑ Kutchan TM, Hampp N, Lottspeich F, Beyreuther K, Zenk MH: The cDNA clone for strictosidine synthase from Rauvolfia serpentina. DNA sequence determination and expression in Escherichia coli. . In: FEBS Lett . . 237 (1-2), 1988, pp. 40-44. PMID 3049153 .
- ↑ Yamazaki Y, Sudo H, Yamazaki M, Aimi N, Saito K: Camptothecin biosynthetic genes in hairy roots of Ophiorrhiza pumila: cloning, characterization and differential expression in tissues and by stress compounds. . In: Plant Cell Physiol. . 44 (4), 2003, pp. 395-403. PMID 12721380 .
- ↑ O'Connor SE, Maresh JJ: Chemistry and biology of monoterpene indole alkaloid biosynthesis. . In: Nat Prod Rep . 4, 2006, pp. 532-47. PMID 16874388 .
- ↑ van Der Heijden R, Jacobs DI, Snoeijer W, Hallard D, Verpoorte R: The Catharanthus alkaloids: pharmacognosy and biotechnology . In: Curr. Med. Chem . 11 (5), 2004, pp. 607-28. PMID 15032608 .
- ↑ a b c Ma X, Panjikar S, Koepke J, Loris E, Stöckigt J: The structure of Rauvolfia serpentina strictosidine synthase is a novel six-bladed beta-propeller fold in plant proteins . In: Plant Cell. . 4, 2006, pp. 907-20. PMID 16531499 .
- ↑ PDB 2FP8 , PDB 2FP9 and PDB 2FPC
- ↑ PDB 2FPB