Sichuan-Tibet Railway
| Sichuan-Tibet Railway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route length: | 1629 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Top speed: | 160 km / h – 200 km / h | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
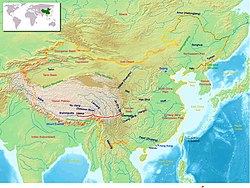
The Sichuan-Tibet Railway or the Sichuan-Xizang Railway ( Chinese 川藏 鐵路 , Pinyin Chuānzáng Tiělù ) is supposed to connect over 1,600 km of Tibet's capital Lhasa directly with the megacity of Chengdu and further with the centers in the east and south-east of China. The completion of the entire route is planned for 2026 or 2030. In addition to the Lhasa Railway , which has been in operation since 2006 , this will be the second railway connection between the autonomous region of Tibet and the heartland of China.
Geographical location
The route leads through the sparsely populated high mountains in the east of Tibet and in the west of the Sichuan province .
history
prehistory
Around a hundred years ago there was already interest on the Chinese side in a rail link to Tibet. Mao Zedong brought the idea back into discussion in the 1950s. In view of the high mountain ranges to be overcome, the technical problems are enormous. The successful construction of the Lhasa Railway, which reaches heights of over 5000 m, encouraged decision-makers to start the project. The cost is estimated at $ 40 billion. The realization takes place in several construction phases, each starting from the two end points.
start of building
In October 2014, the top Chinese planning authority approved the construction of the Sichuan-Tibet railway. In the same year, the first work began in Lhasa and Chengdu. The first section will be the section from Lhasa to Nyingchi (402 km). This section alone, construction of which began in June 2015, will cost approximately USD 6.9 billion. The construction time should be seven years. The client is the China Railway Eryuan Engineering Group, a subsidiary of the state railway company of China.
opening
On December 28, 2018 was on the 141 km long section Chengdu- Ya'an the scheduled operation was added. The section is set up for mixed operation . For passenger trains, there are top speeds between 160 km / h and 200 km / h. Operation started with 10 pairs of trains per day. The fastest run the route with a journey time of 56 minutes. An approximately 400 km long section is to be opened in Tibet in 2021. The opening of the entire route is expected in 2026.
Lines
The route essentially follows the Sichuan-Tibet Highway , which is part of National Road 318 . 14 mountain massifs are crossed, two of which are higher than Mont Blanc . In total, 14,000 meters of altitude have to be overcome. The mountainous country is known for frequent earthquakes, where the Indian and Eurasian continental plates collide. Landslides, snow avalanches, or floods are not uncommon. The region is also ecologically sensitive. The middle section from Kangding to Nyingchi is considered particularly challenging and will be completed last. Around half of the route runs on or in engineering structures . The railway line is designed for a speed of 160 km / h to 200 km / h. The freight capacity should be 10 million tons per year. The travel time from Chengdu to Lhasa is planned to be 13 to 15 hours. Trains between Beijing and Lhasa take 48 hours on the Lhasa Railway. The travel time on the road is three days.
meaning
The railway line will open up an impassable area in terms of traffic and strengthen the connection between Tibet and the Chinese heartland. This will have multiple economic, cultural and political implications for residents along the route. As with the Lhasa Railway, an increase in tourism is also expected. Large forest areas as well as deposits of copper and other raw materials are located in the catchment area. There are also foreign policy interests, the railway line runs near the border with India. The course of the border is controversial here between the two states.
literature
- bac: China is putting numerous new lines into operation . In: Eisenbahn-Revue International 4/2019, p. 186f.
Individual evidence
- ↑ bac: China , p. 187.
- ^ Sichuan Tibet Railway - Under Construction ( en ) tibetdiscovery.com. Retrieved August 27, 2017.
- ↑ a b A new railway to Tibet - Doubling down ( en ) economist.com. May 21, 2016. Retrieved August 27, 2017.
- ↑ a b c China Approves New Railway for Tibet ( en ) CRI. October 31, 2014. Retrieved August 27, 2017.
- ↑ a b China’s $ 37bn railway to Tibet is “world's riskiest” ( en ) GCR Global Construction Review. July 7, 2017. Retrieved August 28, 2017.
- ↑ bac: China , p. 187.
- ↑ Lobsang Tsering: The Most Difficult Segment of Sichuan Tibet Railway Is Expected to Start Construction in 2018 ( en ) tibettravel.org. October 18, 2016. Retrieved August 28, 2017.
- ^ Claude Arpi: The Sichuan-Tibet rail-line on the way ( en ) usually India Defense Review. February 5, 2016. Retrieved August 28, 2017.