Languages of Georgia
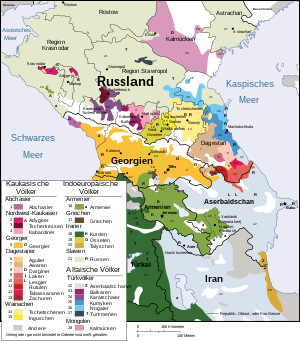
Multi-ethnic Georgia is a country in the Caucasus, which has been known since ancient times to be rich in people and languages . Many ethnic groups live in remote areas and only speak their own language. A total of 20-30 languages from six different language families are spoken in Georgia today.
Georgian is the official language
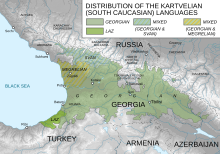
The official language of Georgia is Georgian , which is spoken by around 4 million people. It belongs to the South Caucasian language family and has had its own alphabet since the 5th century . Over 80% of Georgian citizens (3.22 million of 3.71 million inhabitants in 2014) are classified as ethnic Georgians, for which in Georgia traditionally (from the Middle Ages through modern times and Soviet times until today) all speakers of South Caucasian languages are counted, including the approximately 500,000 Mingrelians , the approximately 25,000 Swans and the (on the Georgian side of the border) approximately 2000 Lasen (see adjacent map), because they speak Georgian as a common written language in addition to their own languages and because they belong to the Georgian Orthodox Church .
Other major national languages
Other important languages in the country are also South Caucasian Mingrelian (500,000 speakers), Indo-European Armenian (450,000 speakers), Russian (the number of speakers has fallen sharply since 1991), the Turkic language Azerbaijani (around 300,000 speakers), the the West Caucasian scoring Abkhaz and ostiranische language Ossetian (the latter each have around 100 thousand. speaker).
Languages in Georgia with at least 100,000 speakers
- Georgian 4 million, South Caucasian (Kartwelisch)
- Mingrelian 500,000, South Caucasian (Kartwelisch)
- Armenian 450 thousand, Indo-European
- Russian 400,000, Indo-European, Slavic
- Azerbaijani 300k, Turkish
- Abkhazian 100 thousand, West Caucasian
- Ossetian 100,000, Indo-European, Iranian
Classification of the languages spoken in Georgia
The languages of Georgia belong to six different language families. Three of them - South Caucasian, West Caucasian and East Caucasian - are considered to be autochthonous Caucasian languages . From today's point of view, these three groups are not related to one another. The three other language families - Indo-European , Turkic and Afro-Asian - include the languages whose carriers immigrated to the Caucasus only later (Armenians since the 7th century BC). The following classification describes the relationships and the number of speakers of all languages spoken in Georgia.
Note on the number of speakers: They refer exclusively to the speakers of these languages in Georgia . "S2" includes native speakers and speakers who have learned this language.
-
South Caucasian (Kartwelisch) A total of 4.5 million speakers in Georgia
-
Kartuli
-
Georgian (Kartuli, Grusinisch) (4 million speakers, S2 5 million)
- Dialects : Imeretic, Letschchumisch, Gurianisch, Ajarisch, Imerchev (in Turkey), Kachetisch, Ingilo (in Azerbaijan), Tush, Chevsur, Mochev, Pschav, Mtiul, Feredjan (in Iran), Mes'chur-Javachuri. Judeo-Georgian .
-
Georgian (Kartuli, Grusinisch) (4 million speakers, S2 5 million)
-
Sanisch
- Mingrelian (500,000)
- Lasisch (Tschanisch) (2,000, significantly more in Turkey)
-
Swan
- Swan (15-30,000)
-
Kartuli
-
West Caucasian A total of 100,000 speakers in Georgia
-
Abkhazian-Abasinian
- Abkhazian (100,000) dialects: Bzyb, Abschui, Samurzakan.
-
Abkhazian-Abasinian
-
East Caucasian A total of 10,000 speakers in Georgia
- Nachisch
- Dagestani
- Indo-European A total of 700,000 (with S2 1.2 million) speakers in Georgia
-
Turkish A total of 400,000 speakers in Georgia
-
Oghusian
- Azerbaijani (300,000)
- Urumian (100,000) (Turkish dialect, spoken by ethnic Greeks)
- Turkish (Ottoman) (3,000)
-
Kipchak
- Tatar (3,000)
- Jewish-Crimean-Tatar (few speakers)
-
Oghusian
-
Afro-Asian Only 4,000 speakers left in Georgia
-
Semitic
-
Aramaic
- Bohtan New Aramaic (around 1,000)
- Aisor ( Assyrian-New Aramaic ) (around 3,000)
-
Aramaic
-
Semitic
The number of speakers comes from Ethnologue (5th edition 2005), the Fischer Weltalmanach 2006 and the specialist literature on the individual language families. The classification is based on the web link given below. The language families and their branches are shown in bold (only the branches for which there are languages spoken in Georgia are given).
literature
- Klimov, Georgij A .: Introduction to Caucasian Linguistics . By Jost Gippert. Buske, Hamburg 1994, ISBN 3-87548-060-0