Squalene synthase
| Squalene synthase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 417 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer; multipass membrane protein (ER) | |
| Cofactor | Mg 2+ | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | FDFT1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.5.1.21 , transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of a farnesyl residue | |
| Substrate | 2 farnesyl diphosphate + 2 NADPH / H + | |
| Products | Squalene + 2 PP i + 2 NADP + | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Eukaryotes | |
Squalene synthase (SQS) (also: farnesyl diphosphate farnesyl transferase, FDFT) is the enzyme that catalyzes the condensation reaction of two molecules of farnesyl diphosphate to squalene in eukaryotes . This is a sub-step in cholesterol biosynthesis and the first reaction that leads exclusively to cholesterol in animals. It is a transmembrane protein that is located on the endoplasmic reticulum . SQS is a promising pharmacological target for lowering cholesterol levels.
There are homologous enzymes in carotene- producing organisms that condense geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) to phytoene as part of this synthesis .
Catalyzed reaction
The reaction takes place in two sub-steps:
First, two farnesyl diphosphate molecules condense to form prequalene diphosphate.
 + 2 NADPH / H + ⇔
+ 2 NADPH / H + ⇔
⇔ 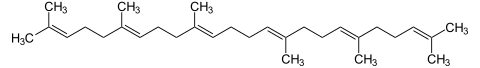 + 2 NADP + + PP i
+ 2 NADP + + PP i
Then presqualene diphosphate is reduced to squalene and rearranged.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Institute of Bioinformatics (EBI): InterPro IPR006449 Farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase. Retrieved August 15, 2011 .
- ↑ UniProt P37268
- ↑ Do R, Kiss RS, Gaudet D, Engert JC: Squalene synthase: a critical enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway . In: Clin. Genet. . 75, No. 1, January 2009, pp. 19-29. doi : 10.1111 / j.1399-0004.2008.01099.x . PMID 19054015 .
Web links
- Jassal / reactome: Two FPP molecules dimerize to form presqualene diphosphate
- Jassal / reactome: Reduction of presqualene diphosphate to form squalene