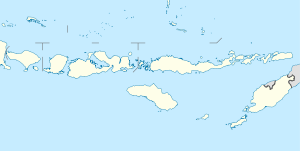
Sumbawa
| Sumbawa | ||
|---|---|---|
| Location of Sumbawa | ||
| Waters | Lake Flores , Sawu , Bali , Indian Ocean | |
| Archipelago | Lesser Sunda Islands | |
| Geographical location | 8 ° 47 ′ S , 118 ° 5 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| length | 280 km | |
| width | 90 km | |
| surface | 15,448 km² | |
| Highest elevation |
Tambora 2850 m |
|
| Residents | 1,330,000 (2010) 86 inhabitants / km² |
|
| main place | Sumbawa Besar , Bima-Raba | |
| Topographic map of Sumbawa | ||
Sumbawa is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands . It is 15,448 km² and has about 1,330,000 inhabitants.
Sumbawa belongs to the Indonesian province of Nusa Tenggara Barat . The western part of the island is called Semawa with the main town Sumbawa Besar . The eastern part is Bima with the main town Bima -Raba.
geography
location
The center of the island is 9 ° south and 118 ° east. Sumbawa is about 280 km long and 15–90 km wide, extends in a west-east direction and covers an area of 15,448 km². To the west of Sumbawa is the island of Lombok and to the east of Flores , with the smaller islands of Komodo and Rinca in between . In the south the Sawu Sea extends with the island of Sumba , in the north the Floressee .
There are many smaller islands around Sumbawa. In the north of the western part, the larger Moyo and the smaller islands Medang and Satonda are upstream. To the southeast of Sumbawa lie Teluk Saleh , Liang , Ngali and Rakiti in Bay . To the northeast of Sumbawa is Sangeang Island . To the northwest are the small islands of Belang , Panjang , Saringi and Airtawar . In the east there is the islet Kelapa .
National nature

The island is mountainous, partly forested and covered with scrubland. Numerous bays shape the coastline.
The ninth largest island in Indonesia is roughly divided into three parts: a western and an eastern part, which are connected by a narrow isthmus, and a peninsula protruding to the north with the 2850 m high volcano Tambora . The eruption of Tambora in 1815 had global effects.
Sumbawa's climate is much drier than that of Lombok or Bali, and agriculture, the main livelihood of the population, is less productive.
Administrative division
Sumbawa consists of four administrative districts ( Kabupaten ) and one city ( Kota ):
| coat of arms | Kabupaten / Kota administrative district / city |
Seat of government | location | Kecamatan districts |
Desa / Kelurahan parishes |
Area [km²] | Population (2011) | Inhabitants / km² (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Kabupaten Bima | Raba |  |
18th | 177 | 4,389.40 | 443,663 | 101 |
 |
Kabupaten Dompu | Dompu |  |
8th | 79 | 2,324.60 | 221.184 | 95 |
 |
Kabupaten Sumbawa | Sumbawa Besar |  |
24 | 166 | 6,643.98 | 419,987 | 63 |
 |
Sumbawa Barat | Taliwang |  |
8th | 65 | 1,849.02 | 116.112 | 63 |
 |
Bima | Raba |  |
5 | 38 | 207.50 | 144.018 | 694 |
population
The 2010 census showed a population of 1.33 million people for Sumbawa including the offshore smaller islands. This corresponds to 29.58% of the population of Nusa Tenggara Barat Province, which had 4.5 million inhabitants. Almost all of the residents of Sumbawa are Muslims. The two largest cities, Bima 142,000 and Sumbawa Besar of 60,000 inhabitants, both the capitals of the districts of the same name are cultural centers of two different ethnic groups, with two very different languages: In the Western District of Sumbawa we speak Bahasa Semawa , however, is in the eastern Bima Bahasa Bima spoken. Because of the relatively dry climate, in which crops are often endangered by droughts, many of Sumbawa's residents work in the Middle East.
With a population density of 86 inhabitants / km², Sumbawa is sparsely populated by Indonesian standards.
Earlier it was in the northeast of Sumbawa Tambora speaking, as most western Papua language applies. After the eruption of the volcano of the same name in 1815, the language died out.
history
Sumbawa has long been known for exporting sandalwood . There used to be three sultanates on the island with their own culture and language: Bima in the east, Tambora in the middle and Sumbawa in the west. In the 17th century, the islands of Sumba , Solor and part of Flores still belonged to the Sultanate of Bima . The western part of the island has long belonged to the territory of the kings of Bali. The Tambora eruption in 1815 wreaked havoc on Sumbawa and claimed over 70,000 lives. As a result, Sumbawa became impoverished and greatly lost in importance. After Indonesia's independence, Sumbawa became part of the Nusa Tenggara Barat province, the capital of which is Mataram on the island of Lombok. However, there are plans to possibly make Sumbawa a separate province.
Economy and Transport
Mining is an important economic factor in Sumbawa, with around 7,000 workers in the Sumbawa Barat district. Gold and copper have been mined in the Batu Hijau mine not far from the small town of Maluk since 2001, although they are further processed on other islands in Indonesia. Most of the workforce is employed in agriculture, which due to the drought is not as productive as on the islands of Indonesia further west. Rice is primarily grown, bananas e.g. B. do not thrive on Sumbawa. Industry is almost completely absent. Tourism is hardly developed and is limited to the southwest coast of Sumbawa, where surfers find favorable conditions.
By far the most important port of Sumbawa is Poto Tano on the west coast, from where several ships leave daily for Labuhan Lombok on the neighboring island of Lombok. In Poto Tano begins a mostly well-developed interurban road that crosses Sumbawa from west to east and on which the most important cities are located. Less good back roads branch off from it to the places on the north and south coast. In particular, the south coast of Sumbawa has insufficient transport links. By far the most important airfield in Sumbawa is located in Bima.
The airport in the main town of Sumbawa Besar was modernized in 2019 and the runway was significantly enlarged to enable larger passenger planes to land.
Individual evidence
- ↑ hans-peter grumpe: Sumbawa 1 - introduction. In: hpgrumpe.de. Retrieved December 30, 2014 .
- ↑ Jumlah Penduduk NTB 4,4 Juta Jiwa ( Memento from July 18, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) In: batukar.info
- ^ Asia: Indonesia (Urban City Population): Provinces & Cities - Statistics & Maps on City Population. In: citypopulation.de. 1980, accessed December 30, 2014 .
- ↑ Pemda Minta Masyarakat Waspadai Ancaman Bencana Kekeringan ( Memento from March 16, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) In: gaungntb.com
- ↑ Stefan Loose: Indonesia from Sumatra to Sulawesi , p. 423. Ostfildern 2013
- ↑ Stefan Loose: Indonesia from Sumatra to Sulawesi , p. 424. Ostfildern 2013
- ↑ Stefan Loose: Indonesia from Sumatra to Sulawesi , p. 427. Ostfildern 2013
- ↑ Dorong kegiatan ekonomi Sumbawa, Bandara Sultan Muhammad Kaharuddin SIAP diresmikan. Retrieved February 19, 2020 .
Web links