Surveillante (ship)
|
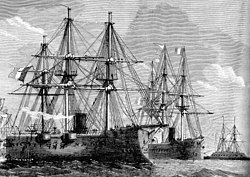
The French Baltic Sea squadron with (from left) the tank frigates Océan and Surveillante as well as the ram Rochambeau
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
The Surveillante was a French armored frigate of the Provence class. In the Franco-Prussian War in 1870 she was the flagship of the Baltic Sea Squadron .
Technical specifications
- Type of ship: tank frigate
- Typ ship: Provence
- Builder: Unknown
- Launched: Unknown
- Size: 5900-6000 t
- Length: 80.72 m
- Width: 17.0 m
- Draft: 7.7–8.4 m
- Drive: steam engine , sails
- Output: 3050–3600 hp
- Speed: 13.0-14.5 kn
- Masts: 3
- Rigging: Bark
- Armor: 102–150 mm
- Armament: 30-16.4 cm guns
history

The Provence- class units entered service from 1865. After the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War, the Surveillante became the flagship of the so-called Ostseegeschwader (French: Escadre du Nord = Nordgeschwader) under Vice Admiral Louis Edouard Bouet-Willaumez in July 1870 . The association arrived in the North Sea on July 29, 1870 . Instead of 14 ironclads as planned , it originally consisted of seven units:
- Surveillante (flagship)
- Gauloise (sister ship)
- Guyenne (armored frigate)
- Flandre (sister ship)
- Océan (armored frigate)
- Thetis (armored corvette)
- Joan of Arc (armored corvette)
- Cassard ( Aviso )
After the ram Rochambeau arrived in the Baltic Sea, the Flandre and the Océan returned to France.
Before continuing to the Baltic Sea, the squadron brought in a good 40 north German merchant ships in the Heligoland area . When it entered the Kattegat at the beginning of August , the news arrived that, contrary to French hopes , Denmark would remain neutral in the war. In the meantime it had been realized that the troops planned for the landing corps on the German Baltic coast were urgently needed in the mother country.
The squadron's deployment was severely hampered by a lack of coal . A certain amount of coal was sold from the English side on Heligoland and from the Danish side, but most of the supplies had to be brought in from Dunkirk . Bouët-Willaumez therefore shifted to an unsuccessful blockade activity off the Mecklenburg and Prussian coast. The blockade of Swinoujscie , Danzig , Pillau and Memel and a bombardment of Kolberg were planned , which did not succeed for various reasons.
On August 17, 1870, the squadron was attacked in a naval battle off Hiddensee by the north German Aviso SMS Grille and the gunboats SMS Blitz , SMS Drache and SMS Salamander , apparently neither causing damage nor losses. On 21/22 On August 1st, the corvette SMS Nymphe carried out a sortie against the blockade forces in the Danzig Bay on the Putziger Wiek , whereby, according to North German information, 18 French seamen died who were buried in Copenhagen .
The squadron began its return journey to France as early as September 1870 and operated again briefly off Heligoland on September 26, 1870, before returning to France on the 29th. The French North Sea squadron under Vice Admiral Martin Fourichon had already withdrawn to France on September 12 due to logistical difficulties, bad weather and in view of the development of the military situation at home.
From October 11th, French ironclads operated again in the North Sea, including the Surveillante . On November 19, her oar broke. She drifted at sea for 48 hours before she could be picked up by the armored frigate Revanche and towed to Cherbourg.
Sister ships
Flandre , Gauloise , Héroine , Magnanine , Provence , Valeureuse .
literature
- René de Pont-Jest: Les escadres françaises dans la Mer du Nord et la Baltique , Paris (Hachette) 1871. German edition: The campaign of 1870 in the North and Baltic Seas. With a map of the Jade-Weser and Elbe estuaries , Bremen (Heyse) 1871.
- Albert Röhr: Handbook of German Navy History , Oldenburg / Hamburg (Gerhard Stalling) 1963.
- Wolfgang Petter: German fleet armor from Wallenstein to Tirpitz , in: Military History Research Office (ed.): German military history in six volumes 1648–1939 , Vol. V, Herrsching 1983, pp. 3–262. ISBN 3-88199-112-3
- Clas Broder Hansen: Germany will become a sea power. The construction of the Imperial Navy 1867–1880 , Graefelfing before Munich 1991. ISBN 3-924896-23-2
- Geoffrey Wawro : The Franco-Prussian War. The German Conquest of France in 1870-1871 , Cambridge (Cambridge University Press) 2003. ISBN 0-521-58436-1