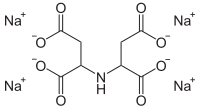
Tetrasodium iminodisuccinate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetrasodium iminodisuccinate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 7 NNa 4 O 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 337.10 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
564 g cm −3 at 25 ° C and pH 13.1 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Tetrasodium iminodisuccinate (also: Iminodisuccinate tetrasodium salt ) is a sodium salt of iminodisuccinic acid , also known as N - (1,2-dicarboxyethyl) aspartic acid is referred to. The salts are called iminodisuccinates (IDS or IDHA).
Extraction and presentation
Iminodisuccinic acid can be prepared by reacting maleic anhydride with ammonia and sodium hydroxide .
When maleic anhydride is reacted with sodium hydroxide in water at an elevated temperature, a concentrated disodium maleate solution is formed, to which ammonia is added. The reaction mixture is heated to temperatures of 90 to 145 ° C, excess water and ammonia are distilled off and with yields of up to 98% of theory. Th. Obtain an aqueous solution with approx. 34% IDS Na 4 salt. A solid mixture can be obtained from this by spray-drying, consisting on average of> 65% IDS-Na salts (mainly IDS-Na 4 salts ), <2% maleic acid Na salts, <8% fumaric acid Na salts, <2% malic acid Na salts and <15% aspartic acid Na salts, and> 15% water. The by-products of the reaction do not affect the complexation capacity or the biodegradability of the IDS.
| product | IDS Na 4 salt | Na 2 fumarate | Na 2 aspartate | Na 2 malat | Na 2 maleate | water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial cleaner | 72.1 | 5.6 | 10.6 | - | - | 8.9 |
| Baypure CX 100/34% | > 33.0 | <2.5 | <7.0 | <0.5 | <0.3 | <59.0 |
| Baypure CX 100 solid | > 65.0 | <8.0 | <15.0 | <2.0 | <2.0 | <15.0 |
| Baypure CX 100 solid G. | > 78.0 | <5.0 | <15.0 | <0.7 | <0.5 | <4.0 |
properties
The solid mixture obtained as a white powder after spray-drying the aqueous solution is, in addition to granules with> 78% IDS Na 4 salt content, a commercially available product (Baypure® CX 100). IDHA is a chelate complexing agent of medium complex stability (10 −16 ), which, as a pentadentate ligand, encloses alkaline earth and polyvalent heavy metal ions with one molecule of water in an octahedral structure. In 0.25% aqueous solution, the IDS Na 4 salt has a pH of 11.5 . The salt is stable for several hours in a weakly acidic solution (pH> 4-7) even at 100 ° C and for weeks in a strongly alkaline solution even at an elevated temperature (50 ° C). The IDS Na 4 salt is classified as easily biodegradable according to the OECD methods OECD 302 B (100% after 28 days) and OECD 301 E (78% after 28 days). From the class of widespread chelating agents , only nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), which is suspected of being carcinogenic , and the chelating amino acid derivatives β-alanine diacetic acid and methyl glycine diacetic acid (Trilon M®) are sufficiently biodegradable under certain conditions.
use
Iminodisuccinic acid has been available from Lanxess as a complexing agent under the trade name Baypure CX 100 since 1998 . It reacts with the calcium and magnesium ions (hardeners) in the water and forms chelate complexes in the medium stability range. These prevent the formation of insoluble salts (deposits) and soaps ( lime soaps ) and thus improve the effectiveness of detergents and dishwashing detergents, hand soaps and shampoos. This means that the amount of conventional builders in solid detergents (carbonates, silicates, phosphates, citrates, zeolites) can be reduced or replaced. The calcium binding capacity for IDS Na 4 salt is approx. 230 mg CaCO 3 / g Na salt and is between the capacity of DTPA Na 5 salt (210 mg CaCO 3 / g Na salt) and EDTA Na 4 - Salt (280 mg CaCO 3 / g Na salt).
Most of the other uses of IDS sodium salt are based on the complexation of alkaline earth and heavy metal ions, e.g. B. in industrial cleaners to remove biofilms and limescale deposits, cosmetics, in electroplating, in construction ( setting retarder ), textiles (protection against graying ) and paper. The addition of IDS sodium salt instead of the common phosphonates to solid detergent formulations inhibits the heavy metal-catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in washing liquors containing bleach.
Complexes with Fe 3+ , Cu 2+ , Zn 2+ and Mn 2+ ions are used as micronutrients that provide trace elements that are important for plants in a readily absorbable form; both granulated as soil fertilizer and dissolved as a foliar spray. The common complexing agents for trace elements, such as B. EDTA , DTPA (diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid), EDDHA (ethylenediamine-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid) or HBED ( N , N '-di (2-hydroxybenzyl) -ethylenediamine N , N ' -diacetic acid) are all sparingly until virtually nonbiodegradable . IDHA trace element complexes, on the other hand, offer an interesting alternative.
Stereoisomerism
The manufacturing process from the achiral starting materials produces a mixture of three epimers : (R, R) -iminodisuccinate, (R, S) -iminodisuccinate, and (S, S) -iminodisuccinate. The two meso compounds [R, S] and [S, R] are identical. In the first two cases, the enzymatic breakdown produces D-aspartic acid and fumaric acid, in the latter case L-aspartic acid and fumaric acid, which are further metabolized.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Van Iperen International: IDHA-chelates
- ↑ a b Nu-Calgon: Page no longer available , search in web archives: Safety data sheet ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Lanxess: Baypure CX 100/34% ( Memento of the original from December 10, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Safety Data Sheet.
- ↑ a b c nicnas.gov.au: Aspartic acid, N- (1,2-dicarboxyethyl) -, tetrasodium salt ( Memento of the original from February 12, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked . Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , August 2002.
- ↑ a b c d D. Kołodyńska, H. Hubicka, Z. Hubicki: Studies of application of monodisperse anion exchangers in sorption of heavy metal complexes with IDS. In: Desalination. Volume 239, No. 1–3, pp. 216–228, doi: 10.1016 / j.desal.2008.02.024 .
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of tetrasodium; 2- (1,2-dicarboxylatoethylamino) butanedioate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on July 28, 2019, is shown, which is derived from a self-classification by the distributor .
- ↑ a b Dorota Kołodyńska: Chelating Agents of a New Generation as in Alternative to Conventional chelator for heavy metal ion removal from Different Waste Waters . In: Robert Y. Ning (Ed.): Expanding Issues in Desalination . InTech, 2011, ISBN 978-953-307-624-9 , pp. 339-370 , doi : 10.5772 / 21180 (here: p. 344).
- ↑ Patent US6107518 : Preparation and use of iminodisuccinic acid salts. Published on August 22, 2000 , applicant: Bayer AG, inventors: Torsten Groth, Winfried Joentgen, Paul Wagner, Frank Dobert, Eckhard Wenderoth, Thomas Roick.
- ↑ a b c d e f Lanxess AG, General Product Information : Baypure
- ↑ a b ADOB: Biodegradable chelates
- ^ E. Sanchez et al .: Iminodisuccinate Pathway Map , Manchester College, April 17, 2013
