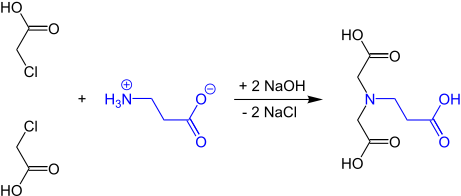
β-alanine diacetic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
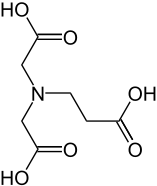
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | β-alanine diacetic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 11 NO 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 205.17 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
190–200 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
water soluble |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
β-alanine diacetic acid or β-ADA (β-alanine diacetate) , the trianion of N - (2-carboxyethyl) iminodiacetic acid, is a tetradentate complexing agent , the stable 1: 1 chelate complexes with cations with a charge number of at least +2, e.g. B. forms the "water hardness builders" Ca 2+ or Mg 2+ . β-alanine diacetic acid should not be confused with α-alanine diacetic acid, also called methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA) or α-ADA, whose alkaline earth and heavy metal complexes are like those of the homologous β-ADA, but in contrast to chelate complexes with conventional complexing agents, such as. B. EDTA , are biodegradable.
presentation
The first synthesis of β-alaninediacetic acid from β-alanine and monochloroacetic acid was reported in 1949 by Gerold Schwarzenbach .
With β-alanine as starting material, the double cyanomethylation with formaldehyde and alkali metal cyanides and hydrolysis of the bis-methyl cyanide formed as an intermediate and subsequent acidification with mineral acids yields β-ADA in yields of only 80%, but very high purity of 99.8%.
The cyanoethylation of iminodiacetic acid with acrylonitrile gives the cyanoethyl compound in the sense of a Michael addition , which after alkaline hydrolysis and acidification gives β-ADA in a total yield of 93.6% and a purity of 99.9%.
In the analogous reaction with acrylic acid esters , 99.9% β-ADA are obtained in an overall yield of 97.6% after acidification.
The most direct route is via the Michael addition of acrylic acid to iminodiacetic acid, which produces the trisodium salt of β-ADA in 97% yield and 99.2% purity. The conversion to β-alaninediacetic acid is not described in this patent.
The most economical synthetic route starts from iminodiacetic acid , which is easily accessible through the oxidation of diethanolamine and serves as the key raw material for the herbicide glyphosate .
properties
β-alanine diacetic acid is a colorless solid which, in sewage treatment plant simulations, was shown to be very readily degradable (98% after eight weeks) and was extremely low in toxicity. Elsewhere, the poor microbial degradability and adsorbability of β-ADA is pointed out. The contradicting assessment of the degradability of β-ADA, the weaker complex formation compared to the (rapidly biodegradable) methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA, Trilon M) and the lower stability in wide temperature and pH ranges are the main reasons for the breakthrough of MGDA as the most suitable substitute for EDTA contributed.
use
Like other complexing agents from the aminopolycarboxylic acid class , β-alanine diacetic acid is found due to its ability to form stable chelate complexes with polyvalent ions, especially the water hardness constituents Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ , as well as transition and heavy metal ions such as Fe 3+ , Mn 2+ , Cu 2+ etc. Use in water softening, in detergents and cleaning agents, in electroplating, cosmetics, paper and textile production.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on BETA-ALANINE DIACETIC ACID in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on April 18, 2020.
- ↑ a b SAA Pedia: N, N-bis (carboxymethyl) -beta-alanine
- ↑ Entry on N- (2-carboxyethyl) iminodiacetic acid at TCI Europe, accessed on June 5, 2017.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ G. Schwarzenbach, H. Ackermann, P. Ruckstuhl, Complexone XV. New derivatives of iminodiacetic acid and its alkaline earth complexes. Relationships between acidity and complex formation , Helv. Chim. Acta , 32, 1175-1186, doi: 10.1002 / hlca.19490320403 .
- ↑ Patent EP490228 : Process for the production of beta-alaninediacetic acid and its alkali metal salts. Published on December 14, 1990 , Applicant: BASF AG, inventor M. Zipplies et al ..
- ↑ a b Patent EP641310B1 : Process for the production of β-alaninediacetic acid or its alkali metal or ammonium salts. Published on January 15, 1997 , Applicant: BASF AG, inventor M. Kneip et al ..
- ↑ Patent EP0356972B2 : Process for the production of beta-alaninediacetic acid or its alkali metal or ammonium salts. Published on April 2, 1997 , Applicant: BASF AG, inventor R. Baur et al ..
- ↑ L. Nitschke, A. Wilk, C. Cammerer, G. Lind, G. Metzner: Biodegradation and aquatic toxicity of β-alaninediacetic acid (β-ADA) . In: Chemosphere . tape 34 , no. 4 , February 1997, p. 807-815 , doi : 10.1016 / S0045-6535 (97) 00009-X .
- ↑ Hessian State Office for Environment and Geology, 6.12 Complexing Agents, p. 12/3, 2003.
- ↑ Environmental Protection Agency, DfE's Safer Chemical Ingredients List, Chelating Agents , Alanine, N, N-bis (carboxymethyl) -, sodium salt (1: 3) .