Thiotepa
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
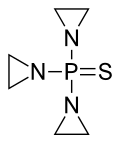
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Thiotepa | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
N , N , N -triethylenethiophosphoric acid triamide |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 12 N 3 PS | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 189.22 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
54-57 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Thiotepa is an alkylating cytostatic agent , which was introduced as early as 1953 for the treatment of cancer diseases ( breast cancer , bladder cancer , ovarian cancer ). It is still used in oncology to this day .
In 2010, Thiotepa was approved throughout the EU - in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents - to prepare patients for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for the treatment of certain blood disorders (e.g. leukemia ) and for the treatment of solid tumors if HSCT is subsequently performed ( trade name TEPADINA ® , pharmaceutical company ADIENNE Pharma & Biotech ).
Thiotepa was originally developed as an auxiliary substance in cotton production.
It is a crystalline, white powder with a melting point between 54 and 57 degrees Celsius. Thiotepa is only stable for a few days in solutions and must therefore be stored at low temperatures.
In the human and animal organism, thiotepa is converted to the likewise alkylating TEPA (triethylenephosphoric acid triamide).
The use of thiotepa leads to significant side effects. These include anemia and a carcinogenic effect, since leukemia can be induced. Bone marrow toxicity is also known for thiotepa.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Thio-TEPA data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Sean M. Gallagher, Steven H. Selman: From the battlefield to the bladder: The development of thioTEPA . In: World Journal of Clinical Urology . tape 3 , no. 3 , November 24, 2014, p. 195–200 , doi : 10.5410 / wjcu.v3.i3.195 ( wjgnet.com [accessed December 31, 2018]).
- ↑ Tepadina® (thiotepa) - New Drug Approval. Accessed December 31, 2018 .
- ↑ Information on Tepadina on the website of the European Medicines Agency .
literature
- Sykes, MP. et al. (1953): Clinical Studies of triethylenephosphoramide compounds with nitrogen mustard-like activity . Cancer 6 (1); 142-48
- Maanen, MJ. et al. (2000) . Chemistry, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of N, N ', N' -triethylenethiophosphoramide (thiotepa) Cancer Treat Rev . 26 (4); 257-68; PMID 10913381
- Hagen, B. et al. (1990): Long-term pharmacokinetics of thio-TEPA, TEPA and total alkylating activity following iv bolus administration of thio-TEPA in ovarian cancer patients . Cancer Chemother Pharmacol . 25 (4); 257-62; PMID 1688514