Trichomonas
| Trichomonas | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Trichomonas vaginalis |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Trichomonas | ||||||||||||
| Dujardin , 1841 |
Trichomonas is a genus of single-celled , 4 to 30 µm large organisms within the eukaryotes . Trichomonas spp. are partially harmless commensals , but some representatives are pathogens in humans and animals.
features
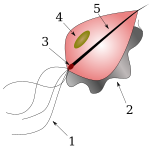
The pear-shaped representatives of the protozoa have four flagella pointing forwards (1 ) and a dragging flagella pointing backwards (2). The flagella are anchored to kinetosomes (3) and encased in a three-layer plasma membrane. The dragline is designed as an undulating (corrugated) membrane. An axial rod emerges from the plasma membrane at the pointed end of the cell body (5). Since the genome of the trichomonads is in the form of chromosomes in a cell nucleus (4), they belong to the eukaryotes .
Trichomonads do not have mitochondria for energy production, but so-called hydrogenosomes . The reproduction takes place by simple longitudinal division, different forms of development as with other protozoa do not occur.
Types (selection)
- Trichomonas tenax , harmless commensal in thehuman oral cavity
- Trichomonas vaginalis , which causes a sexually transmitted vaginal infection ( trichomoniasis ) in humans
- Trichomonas anatis , intestinal parasite in ducks
- Trichomonas buttreyi , parasite in the appendix and colon in pigs
- Trichomonas canistomae , commensal of the oral cavity in dogs
- Trichomonas equibuccalis , commensal of the oral cavity in horses
- Trichomonas felistomae , commensal of the oral cavity in cats
- Trichomonas gallinae , parasite in the upper digestive tract of chickens, pigeons, wild birds, e.g. B. as the cause of the finch dying in 2009 in Northern Germany → yellow goiter
- Trichomonas gallinarum , parasite in the cecum of chickens
- Trichomonas hominis , an intestinal parasite similar to Giardia intestinalis
- Trichomonas microti , parasite in the cecum of rodents
- Trichomonas pavlovi , parasite in the large intestine of cattle
literature
- Ekkehard Wiesner and Regine Ribbeck (Hrsg.): Lexicon of veterinary medicine . 4th edition. Hippocrates, 2000, ISBN 978-3777314594 .
- Hof and Dörries: Dual Series of Medical Microbiology . 3. Edition. Thieme, 2005.
Web links
- Trichomonas Tutorial (English)
- The cause of the finch death is clear. NABU: Do not feed or water birds in summer (risk of spreading), July 21, 2009