Triphosgene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
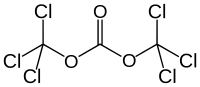
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Triphosgene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 Cl 6 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish solid with an unpleasant odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 296.74 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.6 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
77-81 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
203-206 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
16 hPa (90 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Triphosgene is a powerful poison that forms colorless crystals and is chemically a perchlorinated dimethyl ester of carbonic acid .
Extraction and presentation
Triphosgene can be obtained by chlorinating dimethyl carbonate .
properties
The compound partially decomposes on boiling, releasing phosgene and diphosgene . Chemically, triphosgene behaves similarly to these substances, but all reactions are slower. Today's importance is rather minor. Triphosgene is absorbed through the airways and leads to symptoms similar to pulmonary edema, such as irritation of the throat , nausea, shortness of breath and vomiting. Later on, pulmonary embolism or heart attacks can occur. The eyes are also attacked, so that the eyes must be rinsed out immediately after contamination.
During the First World War , triphosgene was fired as a solid in a mixture with pyridine as a potential warfare agent (" hexa-substance ").
use
As a synthetic chemical, solid triphosgene in solvents can often replace the highly toxic gaseous phosgene. Triphosgene for the preparation of Octalactin B used.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Data sheet bis (trichloromethyl) carbonate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on June 12, 2018.
- ↑ Yao Risheng, Cai Duoli, Han Xiaozha: The Synthesis of Triphosgene by Chlorination of Dimethyl Carbonate (Engl.)
- ↑ P. T. O'Sullivan, W. Buhr, M. A. M. Fuhry, J. R. Harrison, J. E. Davies, N. Feeder, D. R. Marshall, J. W. Burton and A. B. Holmes: Total synthesis of Octalactin B . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society 2004, 126, 2194-2207. (engl.)
