Double piston engine
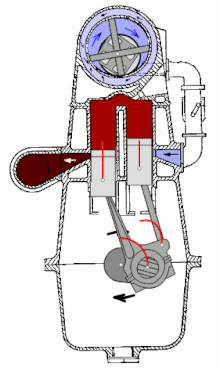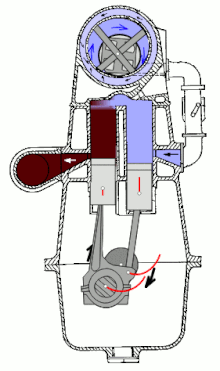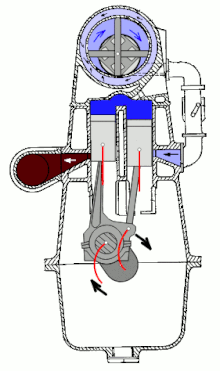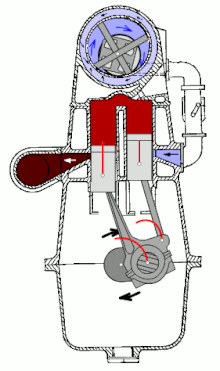
A double piston engine is an internal combustion engine in which two working pistons running in the same direction have a common combustion chamber. The DC flushing used is the only variant in the two-stroke engine that allows the engine to be charged , since the outlet can be closed earlier than the inlet. The double piston engine was mainly used in motorcycles from 1913 to 1970 . Double-piston four-stroke engines are only of historical interest.
Technology and application
In double-piston engines with fork or articulation rods, one piston controls the exhaust process, the other controls the overflow process.
There are three types of double-piston engine:
- The fork connecting rod holds the pistons one behind the other (Puch system)
- The fork connecting rod holds the pistons next to each other (Triumph system)
- The main and secondary connecting rods based on the patent from Arnold Zoller (Zoller system).
Despite the two cylinder liners and pistons, the double-piston engine is one of the single-cylinder engines.
Advantages and disadvantages
- fewer fresh gas losses than with countercurrent purging
- the piston on the exhaust side is not coated with fresh gas, which makes cooling more difficult
- Charging possible if the outlet closes before the inlet.
Manufacturers in motorcycles
- Alberto Garelli (1913-1926)
- Puch ; Developed by Giovanni Marcellino, the pistons run one behind the other (1923–1970)
- Baier ; System Zoller (1927–1929)
- DKW (with piston charging pump); System Zoller (1933-)
- Triumph ; the pistons run side by side (1939 / 1946–1957)
- Jawa 350.
- Manet ; System Zoller (1947–1951)
Manufacturers in passenger cars
- Valveless
- Trojan Limited (1920s)
- Zoller (1934)
Manufacturer in trucks
- Framo Motor U 500 , goes back to the designer Petersen from DKW. Installed in 1943–1951 in the Framo V 501 .
gallery
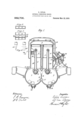
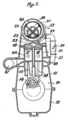
Valveless US Patent US952706A (1909)
Double piston engine - patent drawing by Arnold Zoller (1931)
literature
- Richard van Basshuysen, Fred Schäfer: Handbook Internal Combustion Engine Basics, Components, Systems, Perspectives. 3rd edition, Friedrich Vieweg & Sohn Verlag / GWV Fachverlage GmbH, Wiesbaden, 2005, ISBN 3-528-23933-6 .
- Peter Gerigk, Detlev Bruhn, Dietmar Danner: Automotive engineering. 3rd edition, Westermann Schulbuchverlag GmbH, Braunschweig, 2000, ISBN 3-14-221500-X .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Stefan Knittel: Motorcycle Lexicon. BLV Verlag Zürich, 1981, ISBN 3-405-12226-0 , p. 48
- ↑ a b c d oldtimer-markt.de double piston engine (accessed on May 11, 2013)
- ↑ motor-lit-berlin.de Triumph (accessed on May 11, 2013)
- ↑ US patent 2014678
- ↑ gtue-oldtimerservice.de MANET (accessed on January 4, 2016)
- ↑ motomagazin.cz (accessed on January 4, 2016)
- ↑ Arnold Zoller developed a 6-cylinder, two-stroke, double-piston engine for the racing car in 1934, which was built by the Röhr factory. → roehrauto.de ( Memento from April 29, 2013 in the web archive archive.today ) (accessed on April 11, 2013)
- ↑ Carl-Hans Morgenstern: The two-cylinder two-stroke engine U 500 from Framo-Werke , unpublished manuscript, 1996, Peter Kirchberg