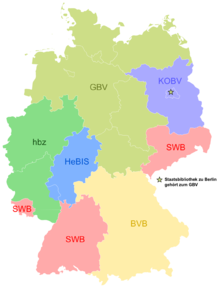
Joint library network
The Common Library Association (GBV) is a German library association of the states of Lower Saxony , Saxony-Anhalt , Thuringia , Hamburg , Bremen , Schleswig-Holstein and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania . In addition to other libraries, the Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation is also a member. The headquarters of the GBV (VZG) is in Göttingen .
Organization of the GBV
The interconnector consists of the participating states and a representative of the Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation (SPK) and other advisory members and permanent guests composed of one representative of the departments and libraries. The group headquarters of the GBV (VZG) in Göttingen acts as the service center for the entire GBV. It hosts the joint union catalog (GVK) for cataloging and research. There are also several specialist working groups (FAG) on selected subject areas. The spokespersons of the specialist working groups, together with the director of the network headquarters and representatives of the libraries and the SPK, form the specialist advisory board , whose task is to coordinate the concepts and plans of the specialist working groups and to coordinate them with the network headquarters. Once a year the place composite conference instead of all libraries with representatives. At the conference, the group management, the group headquarters and the advisory board will present their reports. In addition, the specialist working groups coordinate workshops on current topics. Every three years, the representatives of the various libraries are elected to lead the association.
Additional databases are added, such as the directory of prints from the 17th century published in the German-speaking area ( VD 17 ), maps prints before 1850 (IKAR). etc. hosted. In connection with the research system (GSO), VZG operates systems for interlibrary loan , document delivery and digital libraries . It also supports libraries in setting up and operating local library systems and integrating them into existing university systems. The Verbundzentrale is a Lower Saxony state enterprise with its own budget, 83 employees (as of August 2018) and the six departments of library services , digital library , local library systems , discovery systems , system support and application support .
Tasks and activities
The main task of the network headquarters of the GBV is the cooperation and organization of services from and for libraries in the network area. Above all, this includes the central library system (CBS) for cooperative cataloging and the operation of the local library systems (LBS). For both, the GBV has been using software from the Dutch service provider OCLC (formerly PICA ) since 1993 ; To this end, a cooperation agreement has been concluded in which VZG is also involved in the further development of the library software .
With over 51 million bibliographic records and 97 million proof of ownership, the CBS is the largest cataloging database in Germany. The cataloging is accessed via the WinIBW software. The LBS provides modules for the individual library for their online catalog as well as for user administration, lending and purchasing . For smaller libraries, the network headquarters also offers complete operation of the LBS on central servers as a service. In mid-2014, the LBS service was used by 76 individual libraries. Medium-sized and larger libraries are hosted in a virtualized infrastructure by the VZG.
The network headquarters hosts numerous databases with abstracts and tables of contents and coordinates access to databases from other providers (for example in the case of national licenses ). The library catalogs offered online include the Common Union Catalog (GVK) and the Union Catalog of Public Libraries (ÖVK). The GÖVK is a combined database from the GVK and the ÖVK.
In order to be able to better coordinate the ongoing projects between the association headquarters and the institutions involved in the GBV, the "GBV Association Wiki" was created in 2005 on the basis of MediaWiki . In addition to the GBV committees that document their work here, the libraries and their partners also come together in project-related communities.
The strategic planning and prioritization of projects is determined in the GBV via target and performance agreements and long-term strategy papers.
The Arbeitsgemeinschaft Alte Drucke at the GBV wants to improve the evidence of bibliographical standards for historical prints. It issues a number of recommendations, such as the AAD standard for cataloging old prints up to 1850 , the recommendations for listing provenance , the T-PRO thesaurus for provenance terms , the generic terms for old prints up to 1850 , the recommendations for cataloging prints and the colored paper thesaurus .
At the 103rd Librarians' Day in Bremen in 2014 , the head office of the Joint Library Association (VZG) and the Baden-Württemberg Library Service Center (BSZ) announced a strategic partnership.
history
The forerunner of the joint library network is the Lower Saxony library network, which was founded in 1982 as a joint cataloging network . The technical infrastructure was provided by the Library Computing Center for Lower Saxony (BRZN), a department of the Goettingen SUB , which was spun off as a network center in early 2001. From the beginning, public libraries were also involved in the collaborative work. External data from the German Library (now the German National Library ), the British Library and the Library of Congress were available for cataloging . The possibility of online interlibrary loan was created early on . After signing a contract with the Dutch Pica Foundation in October 1991, the company switched to the Central Network System (CBS) in 1993, to which all local library systems (LBS) were subsequently linked. In 1994, first Saxony-Anhalt and shortly afterwards Thuringia joined the Lower Saxony library network. The joint library network was finally formed in 1996 through the union with the North German Library Association (NBV) with the federal states of Hamburg, Bremen, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Schleswig-Holstein. To this end, the federal states involved signed an administrative agreement in which the organization of the GBV is laid down. The directors Reiner Diedrichs and Stefan Gradmann initially managed the new association together before Reiner Diedrichs took over the overall management. At the beginning of July 1999 the Berlin State Library joined the association; it was followed in 2003 by the entire Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation. The GBV now also offers its services to other libraries outside the network area through service contracts. Associated libraries include the Potsdam University Library (since 2002), libraries from various private universities ( Hertie School of Governance , ESMT European School of Management and Technology, etc.) as well as libraries from various institutes of the Max Planck Society and the Leibniz Association .
literature
- Reiner Diedrichs, Ute Sandholzer: The Common Library Network GBV. In: Bibliothek 25, 2001, pp. 39–48 ( PDF )
- Strategic planning of the GBV 2011–2015 . January 2010 (PDF)
Web links
- Official website
- Literature from and about the joint library network in the catalog of the German National Library
- Literature from and about the joint library network in the bibliographic database WorldCat
Individual evidence
- ↑ Verbund headquarters Göttingen. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ↑ GVK - Common Union Catalog. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ^ Committees of the GBV. GBV, accessed July 6, 2017 .
- ^ Joint conferences of the GBV. GBV
- ↑ Services for Local Library Systems (LBS). GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ↑ Databases hosted by the VZG. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ^ ÖVK - Union Catalog of Public Libraries. GBV, accessed April 12, 2018 .
- ↑ GÖVK - Combined database from GVK and ÖVK. GBV, accessed April 27, 2018 .
- ↑ GBV Verbund-Wiki. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ↑ Target and performance agreements as well as strategic planning of the GBV. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ↑ Working group on old prints at the GBV. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ^ Recommendation of the AAD at the GBV. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .
- ↑ GBV-BSZ cooperation. Retrieved July 21, 2015 .
- ^ Administrative agreement on the establishment of a library network. GBV, accessed September 5, 2011 .