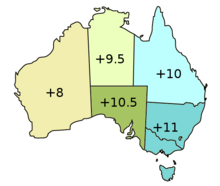
Time zones in Australia
Time zones have existed in Australia since the 1890s, when the colonies of that time defined a respective standard time. Before that, the individual locations could determine their respective local time as local mean time .
The continental part of the country has three time zones: a western ( UTC + 8 ), a central ( UTC + 9: 30 ) and an eastern ( UTC + 10 ). In addition, most of the outer islands have their own time zones.
The proper names of the time zones vary. In the international context, they are usually called Australian Western Standard Time (AWST), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST) and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST). In Germany, the term "Australian" is mostly omitted.
The states and territories in the south and southeast of the country use daylight saving time , but Western Australia , the Northern Territory and Queensland do not .
The standardization of time in Australia began in 1892 when surveyors from all the Australian colonies gathered in Melbourne for the Intercolonial Conference of Surveyors . The delegates accepted the recommendation of the International Meridian Conference of 1884 to use Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as the basis for time zones with hourly differences. In 1895 the corresponding laws came into force in all colonies. South Australia originally took UTC + 9 as its time zone, but changed that to UTC + 9: 30 in 1899 .
When new territories (Northern Territory and Australian Capital Territory ) were formed, the affiliation of the areas to the respective time zone was not changed.
Standard time zones
States and Territories
Western Standard Time (AWST) - UTC + 8
Central Standard Time (ACST) - UTC + 9: 30
Eastern Standard Time (AEST) - UTC + 10
Outdoor areas
Australia's outer areas mostly have their own time zones.
| Outdoor area | Standard time | Summertime |
|---|---|---|
|
|
UTC + 5 | no |
|
|
UTC + 6: 30 | no |
|
|
UTC + 7 | no |
|
|
UTC + 10: 30 | UTC + 11 |
|
|
UTC + 11 | no |
In the internationally not recognized Australian Antarctic Territory - depending on the station - UTC + 6 , UTC + 7 or UTC + 8 is used.
Anomalies
The town of Broken Hill (or the associated cadastral district of Yancowinna County ) in the far west of New South Wales has the same time as South Australia .
Some settlements on the Eyre Highway (namely Eucla , Caiguna , Cocklebiddy , Madura , Mundrabilla and Border Village, as well as the neighboring Pastoral Stations) in the southeastern corner of Western Australia unofficially use UTC + 8:45, which is in the middle between western and central time zones lies. Summer time is also observed in this area, but the total population is only around 200 people.
On the railway line between Kalgoorlie (in Western Australia) and Port Augusta (in South Australia) (on the train and in Cook (South Australia)) the so-called "Train Time" applies: Western Australian time +60 minutes, i.e. UTC + 9.
Summertime
It is up to the individual states and territories to decide whether or not to use daylight saving time. Only during the First and Second World Wars was daylight saving time carried out across the country. In 1968 it was reintroduced into Tasmania , and other southeastern states followed suit.
In New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, Tasmania and South Australia it is observed from the first Sunday in October to the first Sunday in April each year. Such a standardization was decided on April 12, 2007; before that, summer time had started earlier in Tasmania to the south.
On the Australian continent there are five instead of three time zones during this period. The time in South Australia is UTC + 10: 30 , called Central Summer Time (CST) or Central Daylight Time (CDT) (also with the prefix "Australian", ACST or ACDT). The Southeast states use UTC + 11 with the abbreviations EST, EDT, AEST or AEDT.
As a result, there are three places in Australia where New Year's Eve can be celebrated three times (from east to west) due to the adjoining time zones : Cameron Corner , Poeppel Corner and Surveyor Generals Corner .
Debates
In Queensland, public opinion on the subject of summer time is divided, especially in the border area with New South Wales, the time difference between the states is perceived as a nuisance. Some holiday resorts on the border have therefore unofficially introduced summer time. Queensland and the Northern Territory do not have summer time, not least because the difference in day length has less and less effect as the distance from the equator becomes smaller.
The question is also being discussed intensively in Western Australia, where there have already been four referendums (1975, 1984, 1992 and 2009), but all of them failed. The highest “no” value was achieved in 2009 with 54.57%. Each time had been preceded by a three-year probationary period, so that Western Australia also had a summer time from 2006 to 2009.
Special occasions
On the occasion of the 2000 Olympic Games in Sydney , daylight saving time was introduced on August 27, the only exception being South Australia, which kept the regular date on October 29.
On the occasion of the Commonwealth Games 2006 , the end of summer time was postponed to April 26th.
Norms
Although Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) has been used in practice since the 1990s, Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) was formally the reference point until 2005 . Only then was the reference to UTC adopted as the standard by the states and territories on the recommendation of the Australian National Measurement Institute . This change (which was necessary to compensate for minor fluctuations in the earth's rotation) came into effect on September 1, 2005.
National timeframes
However, in some contexts there is a nationally standardized time, especially in the economy and especially in stock market transactions. The Australian Stock Exchange in Sydney uses AEST as a point of reference, so all forward transactions are effectively related to this time.
In other contexts, the different time zones are taken into account, for example in the case of elections that end two hours later than in the east in Western Australia with standard time. This time difference is also taken into account when making submissions to the Federal Court of Australia .
Trivia
Since the seasons are shifted by half a year compared to the northern hemisphere (Europe, North America), the beginning and end of summer time is also shifted by half a year. In northern winter, Central Europe has normal time ( UTC + 1 ), but Australia has summer and (in the corresponding states and territories) daylight saving time (e.g. in New South Wales: UTC + 11 ). That means a time difference of ten hours. In northern summer, when daylight saving time applies there ( UTC + 2 ), it is winter in Australia and normal time applies (e.g. in New South Wales: UTC + 10 ). This means a time difference of only eight hours. This means that the time difference between Central Europe and Eastern Australia is eight or ten hours , depending on the season . There are also two short periods (late March to early April (one week) and early to late October (four weeks)) in which the time difference is nine hours, as in Australia there are not the same (complementary) dates for the start and end of the Summertime is observed as in Europe .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Time zones in Australia ( memento of the original dated November 12, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. . Australian Government Website, accessed October 4, 2015.
- ↑ Unofficial border shield
Web links
- The Australian National Time System, National Standards Commission Leaflet No. January 8, 2003 ( Memento from June 2, 2004 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 226 kB) (English)
- History of summer time, on the website of the Bureau of Meteorology (English)
- Information page of the Australian Government (English)