( S ) -2-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
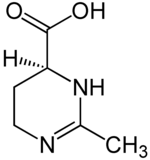
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | (S) -2-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 10 N 2 O 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless powder |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 142.2 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
280 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
good in water (390 g l −1 ) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
( S ) -2-methyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid (synonym ectoin ) is a natural product belonging to the group of compatible solutes or extremolytes . It is formed by halophilic (salt-loving) bacteria , among other things . These protect themselves from extreme environmental conditions, such as B. strong temperature fluctuations, high salt concentration, dehydration or UV radiation. This enables these extremophilic organisms to survive under such stressful conditions.
Occurrence
Ectoin is one of the most widely used compatible solutes. It was first detected in 1985 in the purple bacterium Halorhodospira halochloris (formerly called Ectothiorhodospira halochloris , from which the common name Ectoin is derived), which came from a salt lake in Wadi El Natrun, Egypt ( Sketan Desert ). Today it is known that ectoine occurs in a wide variety of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
In order to compensate for the osmolytic effect at high salt concentrations and to prevent water loss, these extremophilic bacteria form ectoine in the cytoplasm in very high concentrations. Ectoin serves on the one hand to regulate osmotic stress, on the other hand it protects and stabilizes proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids and cell membranes without interfering with the metabolism of the bacteria.
Properties and effects
Ectoin is a cyclic amino acid. In aqueous solution it is present as a mesomeric-stabilized zwitterion . Ectoin has a hydrating effect and also surrounds neighboring structures such as proteins and cell membranes with a protective layer of water ( preferential hydration ). Studies have shown that this water layer is very stable. It is assumed that, in addition to the formation of hydrogen bonds , other mechanisms are also effective, which are due, among other things, to the zwitterionic character of the ectoin. Ectoin itself does not bond with proteins, nor is it able to penetrate a cell.
Manufacturing
Ectoin can be produced fermentatively, chemically and enzymatically. Today, Ectoin is produced fermentatively on an industrial scale. For this purpose, a specific, non-genetically modified strain of the halophilic bacteria Halomonas elongata is used. The purification takes place with the help of z. B. micro / ultrafiltration, electrodialysis and chromatography. Ectoin is manufactured on an industrial scale, for example, at bitop AG (Ectoin®) in Witten, Germany, and at Merck (RonaCare®) in Darmstadt.
use
Cosmetics and medicine
Ectoin has a moisturizing effect and stabilizes the natural structure of biopolymers such as proteins , nucleic acids and biomembrane . It is therefore used in cosmetic care to protect the skin from damage caused by stress factors such as UV radiation, dryness, fine dust or allergens. It is also said to reduce existing wrinkles and protect the skin from new wrinkles.
Ectoin is also used in medical care - as a medical product - for example for irritation or inflammatory diseases of the skin or mucous membranes. These include colds, allergies, respiratory diseases, dry nose and eyes, mucositis, itching or inflammation of the external ear canal or inflammatory skin diseases such as neurodermatitis, psoriasis or eczema.
Contraindications and undesirable effects
If you are hypersensitive to ectoin, ectoin-containing products must not be used. There are currently no data on the use of ectoin-containing products during pregnancy and breastfeeding. There are no known recurring or persistent side effects. After application to the skin, a temporary, localized burning sensation was observed in individual cases.
Finished preparations
actiMare FACE Anti Aging (D), Ectoin Dermatitis Cream 7% (D), Hylo Protect eye drops (A, D), MedEctoin (D), Olynth Ectomed nasal spray (D), PARI ProtECT inhalation solution (D), Sanactiv antiallergic nasal spray (CH ), Sanactiv antiallergic eye drops (CH), Sanadermil EctoinAcute / EctoinAcute Creme (CH), SOS allergy nasal spray (D), Triofan hay fever / Naturel nasal spray (CH)
biochemistry
Ectoin is used in biochemistry to stabilize biologically active substances such as B. proteins , nucleic acids or cells are used. With the help of ectoin, biologically active substances can be protected during storage (e.g. freezing / thawing) and antibodies or enzymes can be stabilized both in stock solutions and in diluted working solutions (e.g. for PCR ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on ECTOIN in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on December 28, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d e Ectoine data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 15, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b W. Schuh et al .: The crystal structure of ectoine, a new osmoregulatory effective amino acid . Z. Naturforsch. 40c, 780-784 (1985).
- ^ R. Graf, S. Anzali, J. Buenger, F. Pfluecker, H. Driller: The multifunctional role of ectoine as a natural cell protectant. In: Clinics in Dermatology . 26 (4), Jul-Aug 2008, pp. 326-333, doi: 10.1016 / j.clindermatol.2008.01.002 .
- ↑ A. Eichel, J. Wittig, K. Sha-Hosseini, R. Mösges: A prospective, controlled study of SNS01 (ectoine nasal spray) compared to BNO-101 (phytotherapeutic dragées) in patients with acute rhinosinusitis. In: Curr Med Res Opin. 29 (7), Jul 2013, pp. 739-746.
- ↑ U. Sonnemann: The next generation of natural hay fever products. pharmaJournal, 36th (GENERIC) 2013.
- ↑ K. Unfried, U. Sydlik, H. Peuschel, C. Albrecht, A. Bilstein, J. Krutmann: The compatible solute ectoine prevents neutrophilic lung inflammation induced by environmental model nanoparticles in vivo . In: European Respiratory Journal . No. 36 , 2010 ( iuf-duesseldorf.de [accessed October 28, 2016]).
- ↑ K. Unfried, U. Krämer, U. Sydlik, A. Autengruber, A. Bilstein, S. Stolz, A. Marini, T. Schikowski, S. Keymel, J. Krutmann: Reduction of neutrophilic lung inflammation by inhalation of the compatible solute ectoine: a randomized trial with elderly individuals . In: International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease . tape 11 , no. 1 . Dove Press, October 18, 2016, p. 2573-2583 , doi : 10.2147 / COPD.S115061 ( dovepress.com [accessed October 28, 2016]).
- ↑ A. Marini, K. Reinelt, J. Krutmann, A. Bilstein: Ectoine-Containing Cream in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized, Comparator-Controlled, Intra-Individual Double-Blind, Multi-Center Trial. In: Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 27, 2014, pp. 57-65.
