4- (indol-3-yl) butyric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
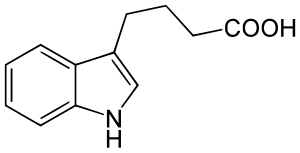
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 4- (indol-3-yl) butyric acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 13 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
whitish, almost odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 203.24 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.36 g cm −3 (bulk density) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
120-123 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
4- (Indol-3-yl) butyric acid ( IBA ) is a naturally occurring phytohormone from the group of auxins in plants . The acid is a light yellow solid with the chemical formula C 12 H 13 NO 2 . It was isolated from corn and willow.
Extraction and presentation
4- (Indol-3-yl) butyric acid can be obtained by heating indole , γ-butyrolactone and sodium hydroxide , followed by neutralization of the intermediate.
use
4- (Indol-3-yl) butyric acid is used as a rooting hormone and growth regulator in plants.
Admission
Indolyl butyric acid has been approved in the United States since the 1960s.
With effect from June 1, 2011, the EU Commission permitted the use of indolyl butyric acid as a growth regulator in ornamental plants. In a number of EU countries, including Germany and Austria, but not Switzerland, pesticides containing this active ingredient are on the market.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i data sheet indole-3-butyric acid (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on March 8, 2013.
- ↑ entry to 3-indolebutyric acid at ChemicalBook , accessed on March 8, 2013.
- ^ Stanley A. Greene: Sittig's Handbook of Pesticides and Agricultural Chemicals . William Andrew, 2005, ISBN 0-8155-1903-6 , pp. 529 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c Entry on 4- (indol-3-yl) butyric acid in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on March 9, 2013.
- ↑ William. G. Hopkins: Introduction to Plant Physiology. John Wiley & Sons, 1999, ISBN 0-471-19281-3 .
- ↑ EPA: Indole-3-Butyric Acid: Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) Fact Sheet (PDF; 35 kB).
- ↑ Directive 2011/28 / EU of the Commission of March 4, 2011 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substance indolyl butyric acid and amending Commission Decision 2008/941 / EC .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Indolylbutyric acid in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 7, 2019.
