Nitrobenzoyl chlorides
| Nitrobenzoyl chlorides | |||||||
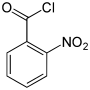
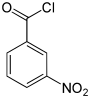
| Surname | 2-nitrobenzoyl chloride | 3-nitrobenzoyl chloride | 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride | ||||
| other names | o -nitrobenzoyl chloride | m -nitrobenzoyl chloride | p -nitrobenzoyl chloride | ||||
| Structural formula |
|
|

|
||||
| CAS number | 610-14-0 | 121-90-4 | 122-04-3 | ||||
| PubChem | 11875 | 8495 | 8502 | ||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 4 ClNO 3 | ||||||
| Molar mass | 185.57 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state | solid / liquid | firmly | |||||
| Brief description | yellow needles or orange liquid |
yellow crystalline solid with a pungent odor |
yellow crystalline powder |
||||
| Melting point | 17-20 ° C | 31-35 ° C | 73 ° C | ||||
| boiling point | 148–149 ° C (9 hPa ) | (Decomp.) | 155 ° C (20 hPa ) | ||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 314 | 312-314 | 314 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||
| 280-305 + 351 + 338-310 |
280-301 + 330 + 331 302 + 352-305 + 351 + 338-310 |
280-301 + 330 + 331 305 + 351 + 338-310-402 + 404 |
|||||
In chemistry , the nitrobenzoyl chlorides form a group of substances that is derived from both benzoyl chloride and nitrobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with attached –COCl group and nitro group (–NO 2 ) as substituents . Their different arrangement ( ortho , meta or para ) results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 7 H 4 NO 3 Cl. The 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride is used in the analysis of organic substances.
presentation
The nitrobenzoyl chlorides are obtained from the nitrobenzoic acids by reaction with thionyl chloride (SOCl 2 ) or phosphorus trichloride (PCl 3 ).
properties
The nitrobenzoyl chlorides are yellowish liquids or crystalline solids with a pungent odor. The 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride, which has the highest symmetry, has the highest melting point. 2-Nitrobenzoyl chloride is thermally unstable. When heated to temperatures above 110 ° C, e.g. B. in vacuum distillation, the compound can decompose explosively.
use
The 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride is mainly used in the analysis of organic substances by derivatization . It is used in cases when a substance in question is more sensitive and direct esterification with 4-nitrobenzoic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid is not possible. As a rule, the reaction takes place in pyridine in order to bind the released HCl immediately.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Roth / Weller: Hazardous chemical reactions, ecomed security, Hüthig Jehle Rehm publishing group, Landsberg / Lech, 31st supplementary delivery 8/2000.
- ↑ a b c data sheet 2-nitrobenzoyl chloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 14, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Entry on 3-nitrobenzoyl chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 12, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Entry on 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on March 12, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Gattermann / Wieland : The practice of organic chemists , 43rd edition, Walter de Gruyter , Berlin · New York 1982, ISBN 3-11-006654-8 , p. 304: " p -Nitrobenzoylchlorid".
- ↑ a b Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 440.
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 424.


