4-nitrobenzoic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 4-nitrobenzoic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 NO 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light green odorless crystalline powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 167.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.61 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
239-242 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
3.42 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very heavy in water (0.42 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−392.2 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
The 4-nitrobenzoic acid is an organic chemical compound and one of the aromatics . The structure consists of a benzene ring with attached carboxy group (-COOH) and nitro group (-NO 2 ) as substituents . It is derived from both benzoic acid and nitrobenzene and belongs to the group of nitrobenzoic acids . 4-Nitrobenzoic acid is mainly used in the analysis of organic substances.
presentation
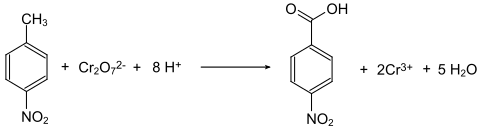
4-Nitrotoluene is oxidized to 4-nitrobenzoic acid with sodium dichromate in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid.
properties
The 4-nitrobenzoic acid is a yellowish crystalline solid. Due to the −M effect of the nitro group, it has a higher acidity than benzoic acid. The pK s value of 3.42 is therefore correspondingly lower (benzoic acid: 4.20).
The heat of decomposition determined by DSC is −373 kJ · mol −1 or −2234 kJ · kg −1 .
use
4-Nitrobenzoic acid is mainly used in the analysis of organic substances by derivatization . Liquid substances or those with a low melting point are converted into easily crystallizing derivatives: alcohols can be identified, for example, by measuring the melting points of their esters of 4-nitrobenzoic acid or 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid . For this purpose, the substance to be analyzed is reacted with 4-nitrobenzoic acid in the presence of small amounts of sulfuric acid.
 Detection of isopropanol as a derivative of 4-nitrobenzoic acid:
Detection of isopropanol as a derivative of 4-nitrobenzoic acid:
4-nitrobenzoic acid-2-propyl ester (melting point: 100.5 ° C.).
The melting points of these derivatives are usually sharp. This implementation is also suitable for numerous amines .
The derivatives of 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid generally have higher melting points than those of 4-nitrobenzoic acid. They are preferred when the melting point of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is too low and an exact determination is no longer possible.
If the substance in question is more sensitive, the direct reaction with the corresponding acid chloride , 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride , takes place instead . In this way z. B. derivatives of amino acids also accessible.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on 4-nitrobenzoic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 14, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Beyer / Walter : Textbook of Organic Chemistry , 19th edition, S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-7776-0356-2 , p. 511.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-34.
- ^ O. Kamm, AO Matthews: p-Nitrobenzoic acid In: Organic Syntheses . 2, 1922, p. 53, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.002.0053 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 392 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ Grewer, T .; Klais, O .: Exothermic decomposition - investigations of the characteristic material properties , VDI-Verlag, series "Humanisierung des Arbeitsleben", Volume 84, Düsseldorf 1988, ISBN 3-18-400855-X , p. 9.
Web links
- Entry to 4-nitrobenzoic acid . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD, accessed December 20, 2013.