Sulfonic acids
| Sulfonic acids and sulfonates |
|---|
 Sulfonic acid |
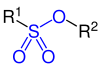 Sulfonic acid ester |
 Sulfonic acid salts |
| R, R 1 and R 2 are organyl groups . The functional groups are marked in blue . |
Sulphonic acids are organic sulfur compounds with the general structure R – SO 2 –OH, where R is an organic radical. Their salts and esters with the general structure R – SO 2 –O - and R 1 –SO 2 –O – R 2 are called sulfonates .
Sulphonic acids and their associated salts and esters are divided into two groups: the aliphatic sulphonic acids or alkane sulphonic acids or sulphonates and the aromatic sulphonic acids or arene sulphonic acids or sulphonates.
Extraction and presentation
There are several synthetic routes for the industrial production of sulfonic acids, some of which are shown here as examples.
A mixture of alkanesulfonic acids is created by the action of sulfur dioxide and oxygen on higher alkanes in the presence of radical formers .
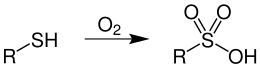
Aliphatic and aromatic sulfonic acids can be synthesized by the oxidation of thiols .
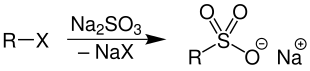
The corresponding sulfonic acid salts are prepared from haloalkanes and sodium sulfite by nucleophilic substitutions .
Arenesulfonic acids are produced by the sulfonation of arenes. There is an electrophilic aromatic substitution . The electrophilic reagent sulfur trioxide is in concentrated sulfuric acid in equilibrium before.
Use and occurrence

Sodium salts of sulfonic acid derivatives are often used as anionic surfactants in cleaning agents. Of the alkylbenzenesulfonates (ABS) with the general formula C n H 2n + 1 –C 6 H 4 –SO 3 - Na + , the most important representative was tetrapropylene benzene sulfonate (TBS) until the 1960s . In the 1950s it had largely replaced soap as a surfactant . However, TBS is (like many representatives of the highly branched ABS) only poorly degraded in wastewater, which u. a. led to mountains of foam on rivers. This is why it was replaced in 1964 by so-called linear alkylbenzenesulfonates (LAS), which have been the most important surfactants in detergent chemistry ever since . In practice, these are often secondary alkyl benzene sulfonates, one of the most widely used being sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate . Others are linear (secondary) alkyl sulfonates (SAS).
Secondary alkyl sulfonic acid esters of phenol are used as plasticizers for PVC , PUR and rubbers .
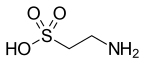
As an aminosulfonic acid, taurine is one of the few naturally occurring sulfonic acids.
p -Toluenesulfonic acid is an important reagent in organic synthesis.
Polymers with sulfonate groups have a special application in water treatment , where they are used in ion exchangers for cations.
Sulphonic acids and their derivatives are also found in tannins and pharmaceuticals. Many dyes also have sulfonate groups in order to achieve high solubility in water.
properties
Alkanesulfonic acids are generally viscous liquids, with the arenesulfonic acids forming hygroscopic crystals. These dissolve easily in water and can be salted out by sodium chloride . Some sulfonic acids form stable, crystalline hydrates. Simple alkanesulfonic acids such as B. methanesulfonic acid are colorless liquids.
In contrast to the esters of sulfuric acid , here there are R – S and not R – O – S bonds. They also differ from the sulfones (R – SO 2 –R '), which do not have a hydroxyl group . Sulfonic acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because the sulfonic group has a stronger electron-withdrawing effect on the hydroxyl group than the carbonyl group , and the proton is thus transferred more easily. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid is even stronger than perchloric acid and thus belongs to the group of super acids .
Reactions
Nucleophilic substitution
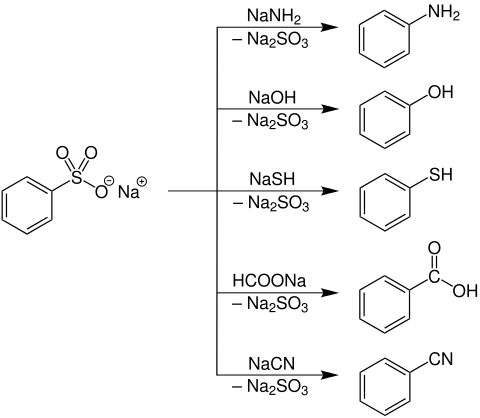
Arene sulfonates can be converted into amines , phenols , carboxylic acids or nitriles at temperatures from 200 to 300 ° C by nucleophilic substitution .
Salt formation
Like sulfuric acid, sulfonic acids are strong acids that form salts with metal hydroxides . In contrast to the corresponding sulfates (salts of sulfuric acid), calcium, barium and lead (II) sulfonates dissolve well in water.
Desulfonation of arenesulfonic acids
The sulfonation of arenes to produce arenesulfonic acids is a reversible reaction . The benzenesulfonic acid specified in the preparation is hydrolyzed to benzene , for example, by dilute hydrochloric acid at temperatures of 150 to 200 ° C :
See also
- Sulfonyl group (here both organic residues are directly bound to the sulfur)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Siegfried Hauptmann: Organic chemistry . German publishing house for basic industry, 1985, ISBN 3-87144-902-4 , p. 480-482 .
- ↑ Joachim Buddrus: Fundamentals of organic chemistry. 4th edition. de Gruyter Verlag, Berlin 2011, ISBN 978-3-11-024894-4 , p. 97.
- ↑ Hans Beyer: Textbook of Organic Chemistry . S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart / Leipzig 1998, ISBN 3-7776-0808-4 , p. 158-160 .